xGen NGS—made to uncover.
FIGYELEM!
IDT termékek szállítási költségei 2024-től:
A szintézis helyétől, valamint a szállítási körülményektől függően az alábbi költségek kerülnek felszámításra:
-
Belgiumból: nettó 6 900 Ft
USA-ból: nettó 34 000 Ft
Belgiumból, szárazjégen: nettó 37 000 Ft
USA-ból, szárazjégen: nettó 45 000 Ft
- Oldatok szállítási költsége: mennyiség és súly függvénye, kérjen ajánlatot a Bio-Science Kft.-től!
Általános tájékoztató az IDT USA gyártási központjából érkező „custom” termékcsoportokról:
szintetikus biológiai termékek:
- Gének
- gBlocks, eBlocks
- Ultramerek
- RNS-oligók
- CRISPR guide RNS-ek
- oPools
qPCR próbák:
a szintézis helye a szekvencia komplexitásától, valamint a választott festék/ quencher kombinációtól függ
szolgáltatások:
- PAGE tisztított termékek
stock termékek:
nem áll teljes lista rendelkezésre, kérjen ajánlatot a Bio-Science Kft.-től!
xGen DNA Library Prep Kit EZ and EZ UNI
- Low input, high complexity—up to 3x fewer duplicates from 1 ng of DNA.
- Improved yield for enrichment—specially formulated PCR master mix boosts yield from a minimal number of PCR cycles.
- High multiplex capability—pre-plated UDI primers enable multiplexing of up to 1536 samples.
- Compatible with xGen Normalase™ Module—streamlines normalization of sequencing libraries from multiplexing
- Workflow design for easy automation
xGen DNA Library Prep MC Kit and MC UNI
- The xGen DNA Library Prep MC Kit is compatible with Covaris® sheared DNA—this kit supports 1 ng to 1 µg, PCR-free libraries from 50 ng input DNA.
- High multiplex capability—pre-plated UDI primers enable multiplexing of up to 1536 samples.
- Compatible with xGen Normalase™ Module—streamlines normalization of sequencing libraries from multiplexing
- Workflow design for easy automation
xGen™ cfDNA & FFPE DNA Library Preparation Kit
High library complexity from low quality samples
The xGen cfDNA & FFPE DNA Library Preparation Kit empowers you with highly complex variant identification from degraded and low-input research samples.
xGen NGS—made for cfDNA & FFPE DNA library preparation.
xGen™ ssDNA & Low-Input DNA Library Preparation Kit
Rescue valuable data from degraded samples
The xGen ssDNA & Low-Input DNA Library Prep Kit enables preparation of libraries from degraded and damaged ssDNA and dsDNA samples in a single reaction. This kit allows users to sequence difficult-to-process samples via unique, proprietary AdaptaseTM technology.
xGen NGS—made for low-input DNA library preparation.
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Unless otherwise agreed to in writing, IDT does not intend for these products to be used in clinical applications and does not warrant their fitness or suitability for any clinical diagnostic use. Purchaser is solely responsible for all decisions regarding the use of these products and any associated regulatory or legal obligations.
Comprehensive coverage
The xGen DNA Library EZ Kit was benchmarked against another supplier of DNA library prep kit that uses enzymatic fragmentation and a widely used HiFi DNA polymerase. Two different libraries for each concentration of input DNA (Coriell NA 12878; 100 ng, 10 ng, and 1 ng) with both kits were generated and evaluated for enrichment using the xGen Pan-Cancer Panel to assess library quality metrics (Table 3). For comparative analysis, identical SPRI®-based size selections (Beckman Coulter) were used for both library prep kits. Libraries were sequenced 2x101 bp on an Illumina® MiSeq® System using v2 chemistry, and reads were normalized to 460k per sample.
The xGen DNA Library EZ Kit required a lower number of PCR cycles to generate yields equivalent to the kit from the alternate supplier. At lower inputs, particularly at 1 ng, the xGen DNA Library EZ Kit provided higher target coverage, a significantly lower percentage of PCR duplicates, and better coverage uniformity compared to the other supplier’s kit. The xGen DNA Library EZ Kit also produced a more uniform insert size across the input quantities evaluated, when compared to the other kit.
Table 3. Targeted sequencing metrics.
| Library prep | Input (ng) | Yield ng/µl (PCR cycles) | Aligned insert (bp) | Duplicates (%) | Mean coverage (%) | 20X Coverage (%) | 30X Coverage (%) | 40X Coverage (%) | 50X Coverage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| xGen DNA Library EZ-sample 1 | 100 | 97 (5) | 235 | 0.78 | 49.1 | 97.3 | 89.4 | 70.9 | 45.9 |
| xGen DNA Library EZ- sample 2 | 95 (5) | 233 | 0.51 | 42.7 | 96.0 | 83.6 | 57.6 | 29.1 | |
| Other supplier, sample 1 | 78 (5) | 211 | 0.35 | 48.5 | 97.2 | 89.5 | 70.0 | 44.1 | |
| Other supplier, sample 2 | 84 (5) | 212 | 0.28 | 41.5 | 95.9 | 82.3 | 54.2 | 25.4 | |
| xGen DNA Library EZ-sample 1 | 10 | 68 (8) | 226 | 1.50 | 48.8 | 97.4 | 89.4 | 69.9 | 44.6 |
| xGen DNA Library EZ-sample 2 | 73 (8) | 223 | 1.17 | 42.5 | 96.0 | 83.0 | 56.2 | 28.7 | |
| Other supplier, sample 1 | 98 (11) | 250 | 1.61 | 47.8 | 96.3 | 86.5 | 66.7 | 42.2 | |
| Other supplier, sample 2 | 91 (11) | 253 | 1.23 | 41.9 | 94.5 | 79.0 | 53.1 | 28.3 | |
| xGen DNA Library EZ-sample 1 | 1 | 78 (11) | 229 | 8.8 | 42.1 | 96.2 | 82.5 | 54.7 | 27.3 |
| xGen DNA Library EZ-sample 2 | 77 (11) | 227 | 6.8 | 37.1 | 93.9 | 73.7 | 39.7 | 13.9 | |
| Other supplier, sample 1 | 100 (17) | 316 | 46.6 | 13.9 | 14.3 | 0.98 | 0.11 | 0.08 | |
| Other supplier, sample 2 | 103 (17) | 315 | 41.5 | 12.5 | 8.89 | 0.42 | 0.09 | 0.06 |
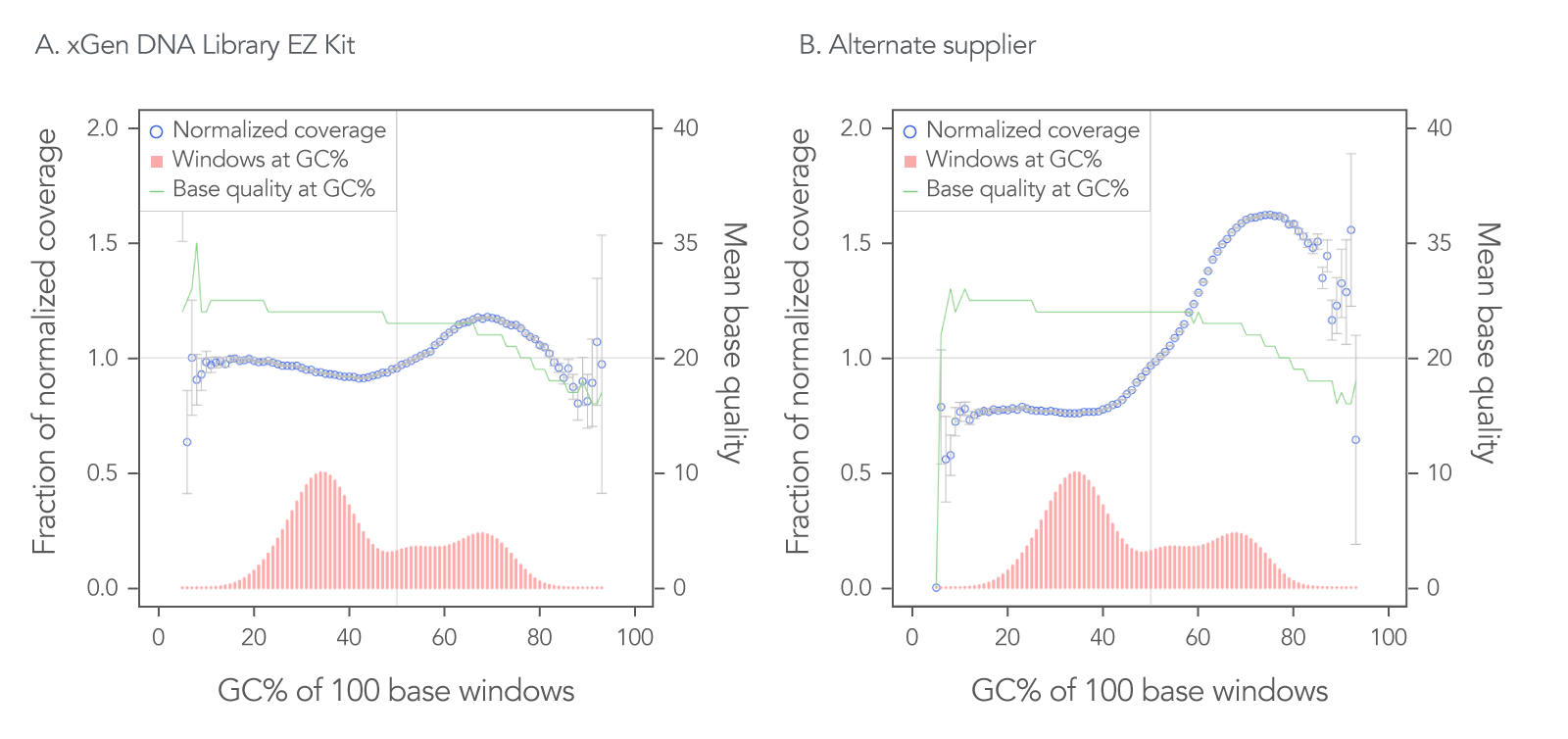
The xGen DNA Library EZ Kit was also benchmarked against another supplier of a DNA library kit using enzymatic fragmentation and 1 ng of DNA harvested from a mock bacterial community (ATCC® MSA-1000®). The DNA was converted into libraries using either the xGen DNA Library EZ Kit or the other enzymatic fragmentation library prep kit. The xGen DNA Library EZ Kit provided a greater library yield from fewer PCR cycles (Table 4), better normalized coverage across distinct GC compositions (Figure 2), improved coverage uniformity (Figure 2), and fewer PCR duplicates (Table 4) compared to the other supplier’s kit.
Figure 2. Higher normalized coverage observed using xGen DNA Library Prep EZ Kit versus another supplier of an enzymatic fragmentation-based library prep kit. To generate the two libraries, the xGen DNA Library EZ Kit (A) and a comparable, enzymatic fragmentation-based library prep kit from another supplier (B) was used on a mock bacterial community (ATCC, MSA-1000) with 1 ng DNA input. For comparative analysis, a 0.65x SPRI-based, DNA cleanup was used after PCR for both kits. The two libraries were sequenced 2x151 bp on an Illumina® MiniSeq® System in High Output mode. Reads were normalized to 5 M per sample. The mock bacterial community contained the following strains: B. cereus (GC% = 35.5), B. adolescentis (GC% = 59.4), C. beijerinckii (GC% = 29.9), D. radiodurans (GC% = 66.7), E. faecalis (GC% = 37.8), E. coli (GC% = 50.8), L. gasseri (GC% = 35.3), R. sphaeroides(GC% = 68.9), S. epidermidis (GC% = 32.0), and S. mutans (GC% = 36.8).
Table 4. Targeted sequencing metrics.
| Library prep kit | Library yield ng/µ L (PCR cycles) | Aligned insert (bp) | Duplicates (%) | Mean coverage (%) | 10X coverage (%) | 20X coverage (%) | 30X coverage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| xGen DNA Library EZ-MSA-sample 1 | 26 (11) | 313.7 | 0.69 | 33.4 | 98.1 | 95.1 | 64.7 |
| xGen DNA Library EZ-MSA-sample 2 | 26 (11) | 319.5 | 0.71 | 33.7 | 98.1 | 95.3 | 65.9 |
| Other supplier, sample-MSA-sample 1 | 4.4 (13) | 321.3 | 2.09 | 32.6 | 98.0 | 86.7 | 48.5 |
| Other supplier, sample-MSA-sample 2 | 4.7 (13) | 328 | 2.29 | 32.8 | 98.0 | 87.0 | 48.6 |
Product data
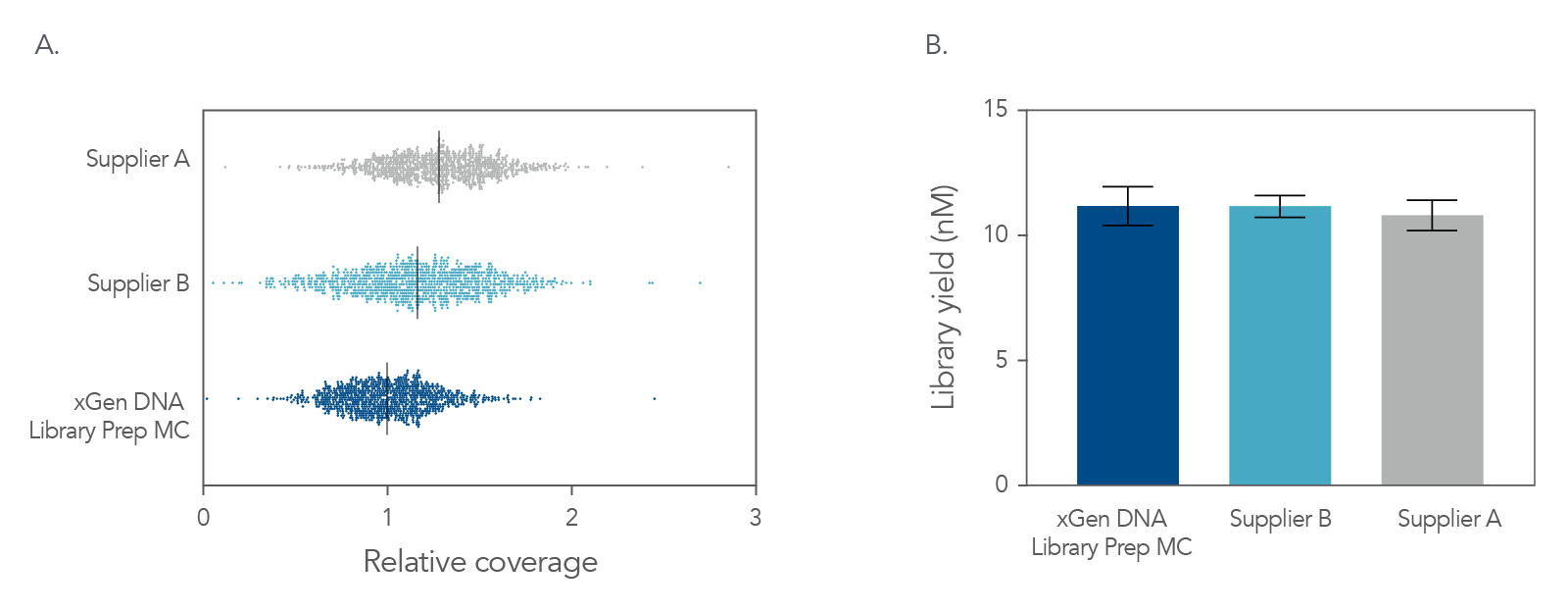
Figure 4. Balanced genome coverage. PCR-free libraries were constructed with the xGen DNA Library Prep MC UNI and two other suppliers’ kits, using 100 ng Coriell NA12878 DNA that was Covaris-sheared to 350 bp, in duplicate. All libraries were constructed using IDT for Illumina® TruSeq® UDI DNA Indexes (Cat. No. 20020590) at supplier-specified concentrations. A consistent bead ratio was used to generate equivalent insert sizes across supplier kits for direct comparison. Libraries were quantified by qPCR and sequenced on an Illumina® NovaSeq ® instrument, and data were normalized to 270 M reads per sample. Right Panel: PCR-free library yields were comparable across all three kits. Left Panel: xGen DNA Library Prep MC UNI showed a more balanced coverage of 971 high GC regions, relative to the mean coverage of other suppliers’ kits that included high GC regions greater than the mean coverage. A deviation from a relative coverage of 1 represents a reduction in coverage uniformity (GC rich bed file from Ross et al, Characterizing and Measuring Bias in Sequence Data; Genome Biol. 2013).
xGen Exome and Pan-Cancer Panels
The xGen DNA Library Prep MC and the two other suppliers’ kits were evaluated with the xGen Pan-Cancer and Exome enrichment panels using duplicate samples of Coriell NA12878 genomic DNA that was Covaris-sheared to 200 bp. A total of 10 ng sheared DNA was used for the xGen Pan-Cancer Panel, and 100 ng sheared DNA was used for the xGen Exome Panel v2. For Pan-Cancer, xGen DNA Library Prep MC and competitor libraries were prepared with truncated Y adapters at supplier-specified concentration and an xGen CDI Primer kit. The Exome libraries were prepared with the xGen DNA Library Prep MC UNI and other suppliers’ kits using IDT for Illumina® TruSeq® UD DNA Indexes (Cat. No. 20020590) at supplier-specified concentration. For both panels, a consistent bead ratio was used to generate equivalent insert sizes across supplier kits for direct comparison. Table 6 lists the experimental results.
The upper section of Table 6 lists data obtained in the following experiment: xGen Pan-Cancer captured libraries were sequenced on a MiSeq® with 100 bp, paired-end reads and were normalized to 1.5 M reads. xGen DNA Library Prep MC Kit yields using the HiFi Master Mix were equivalent to other supplier kits that used Kapa HiFi Hot Start Ready Mix, thus showing library amplification for pre-hyb PCR. Due to MiSeq chemistry, PCR duplicates directly reflect library complexity. All three kits demonstrated similar target coverage, estimated library size, and uniformity of target coverage.
The lower section of Table 6 lists data obtained in the following experiment: Exome capture libraries were sequenced on a NovaSeq® instrument (Illumina) with 150 bp, paired end reads and were normalized to 80 M reads. The xGen DNA Library Prep MC yields using the HiFi Master Mix were equivalent to other supplier kits that used Kapa HiFi Hot Start Ready Mix, thus showing comprehensive library amplification for pre-hyb PCR. Due to NovaSeq chemistry, PCR duplicates include cluster duplicates and do not directly reflect library complexity. However, all three kits showed similar target coverage and uniformity of target coverage.
Table 6. Data from targeted sequencing libraries created with xGen DNA Library Prep Kit MC followed by xGen Pan-Cancer Hyb Panel (upper) or xGen Exome Hyb Panel (lower) capture reactions.
| Prep | Capture run | Input (ng) | Pre-Hyb yield (ng/ul) | Total reads | Mean insert (bp) | Mean coverage | Duplicates (%) | Estimated library | Fold 80 base penalty* | 50X Coverage (%) | 100X Coverage (%) | On-Target (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| xGen DNA Library Prep MC | xGen Pan-Cancer Hyb Panel MiSeq® | 10 | 97.2 | 1.5 M | 201 | 205X | 9.4 | 10 X 106 | 0 | 99.1 | 99 | 80.3 |
| 110 | 201 | 206X | 8.8 | 11 X 106 | 99.1 | 98.9 | 80.3 | |||||
| Supplier A | 101 | 201 | 203X | 9.6 | 10 X 106 | 99.2 | 99 | 80.2 | ||||
| 96 | 201 | 200X | 10.6 | 9 X 106 | 99.2 | 99 | 80 | |||||
| Supplier B | 99.6 | 196 | 203X | 10.1 | 9 X 106 | 99.1 | 99 | 80.3 | ||||
| 105 | 196 | 203X | 9.9 | 9 X 106 | 99.1 | 98.9 | 80.2 | |||||
| XGen DNA Library Prep MC | xGen Exome Hyb Panel NovaSeq® | 100 | 100 | 80 M | 212 | 146X | 9.1 | N/A | 1.53 | 85.6 | 77 | 89.1 |
| 110 | 211 | 146X | 8.2 | 1.48 | 85.9 | 78 | 88.6 | |||||
| Supplier A | 96.5 | 211 | 143X | 9.1 | 1.58 | 85.6 | 76 | 88.7 | ||||
| 101 | 213 | 141X | 9 | 1.54 | 85.8 | 76 | 88.2 | |||||
| Supplier B | 96 | 201 | 145X | 8.2 | 1.57 | 85.6 | 76 | 89.1 | ||||
| 98.4 | 207 | 141X | 9 | 1.55 | 85.8 | 76 | 88.7 |
* Fold 80 Base Penalty is the fold over-coverage necessary to raise 80% of bases in targets to the mean coverage.
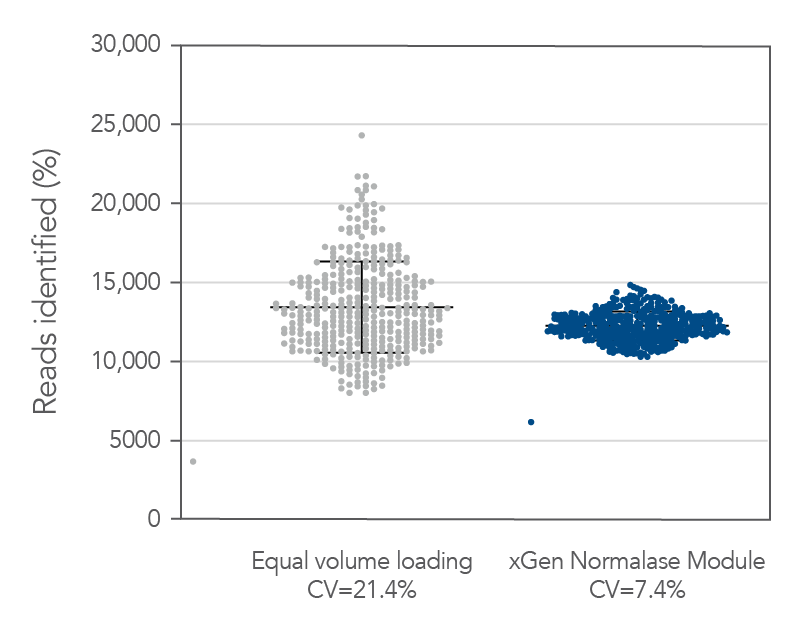
Figure 5. Normalase technology. 384 xGen DNA MC libraries were generated with 1 ng Coriell NA12878 gDNA and were each uniquely indexed with xGen Normalase Unique Dual Indexing primers during library amplification. Libraries were pooled with equal volumes, following PCR. The pool was quantified by Qubit™ (Thermo Fisher) and loaded on an Illumina MiSeq® system to obtain the percent reads Identified from each index. The equal volume pools coefficient of variation (CV) was 21%, showing amplification with the xGen Normalase indexing primers. The same libraries were then enzymatically normalized using xGen Normalase Module to generate an equimolar library pool, at a 4 nM concentration, and were then loaded on an Illumina MiSeq system. The Normalase pool CV as reduced to 7.4%, showing normalization of multiplexed libraries using xGen Normalase technology. Lines represent the median and 95% confidence interval.
Comprehensive metagenomics sequencing
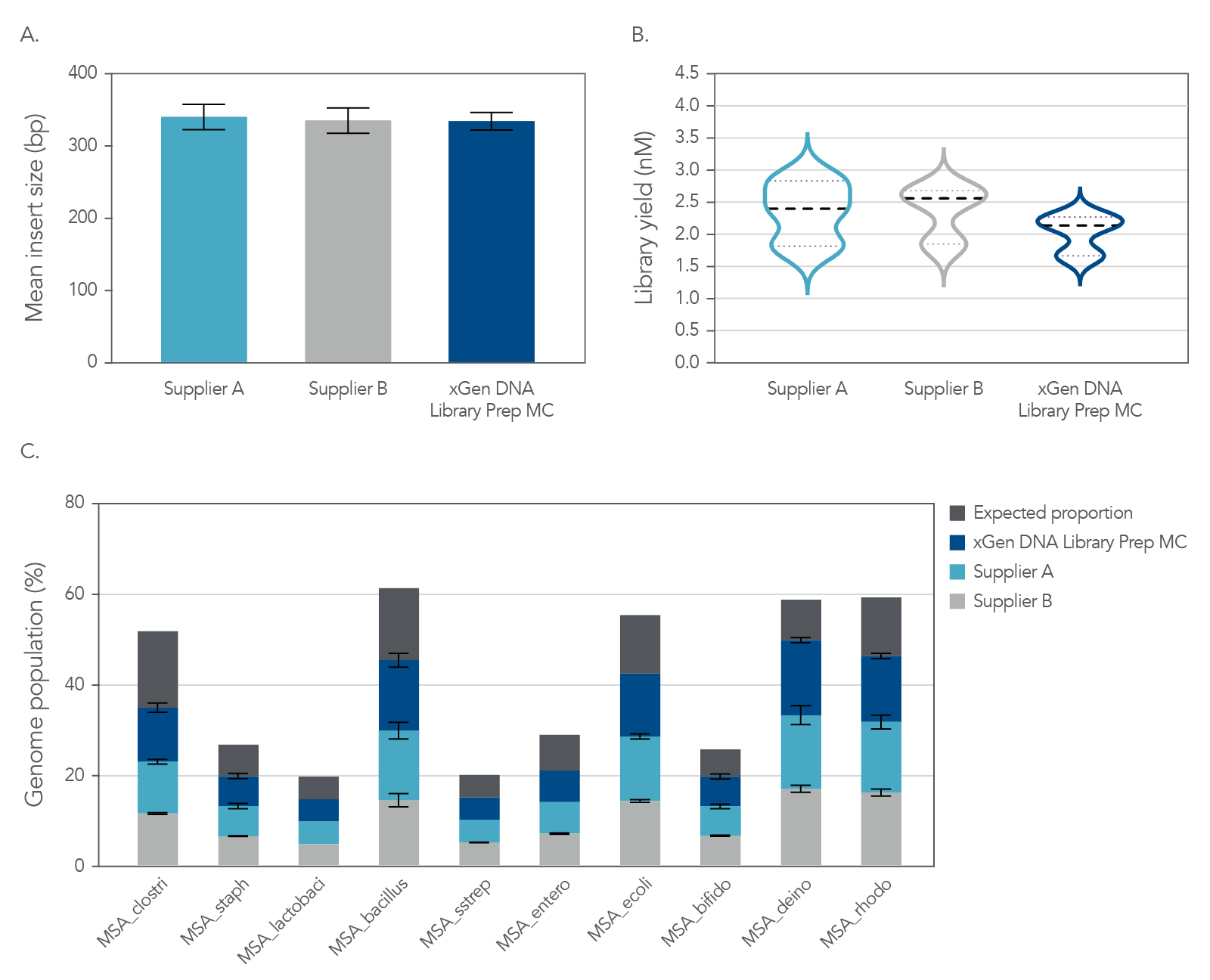
NGS libraries were constructed from 1 ng of mock metagenome DNA (ATCC MSA-1000) that was Covaris-sheared to 350 bp, in duplicate, using xGen DNA Library Prep MC UNI and two other suppliers’ kits. Libraries were prepared using IDT for Illumina TruSeq UDI DNA Indexes (Cat. No. 20020590) at supplier-specified adapter concentrations and were amplified with the polymerase supplied in each kit. Libraries were quantified by Qubit™ (Thermo Fisher) and Agilent Bioanalyzer™ 2100 and sequenced on an Illumina MiSeq system with 150 bp, paired end reads. Data (Figure 7) for each library were normalized to 1 M reads and achieved a metagenome mean coverage of 20X.
Figure 6. Comprehensive metagenomics sequencing. Top panel: Size selecting libraries using the same SPRI ratio resulted in a balanced comparison of the sequencing results. Comparable mean insert sizes and duplication rates were obtained with xGen DNA Library Prep MC UNI and two kits from other suppliers. Bottom panel: Despite significant variation in base composition, the xGen DNA Library Prep MC UNI and the other suppliers’ kits enabled identification of each strain’s genome at the expected frequency, with minimal bias. Variability in GC composition and genome size in this experiment supported that it did not influence results from the xGen™ DNA Library Prep MC UNI kit. The mock bacterial community contained the following strains: B. cereus (GC% = 35.5), B. adolescentis (GC% = 59.4), C. beijerinckii (GC% = 29.9), D. radiodurans (GC% = 66.7), E. faecalis (GC% = 37.8), E. coli (GC% = 50.8), L. gasseri (GC% = 35.3), R. sphaeroides (GC% = 68.9), S. epidermidis (GC% = 32.0), S. mutants (GC% = 36.8).
Comprehensive conversion and error correction enables ultra-low variant identification with cell-free DNA
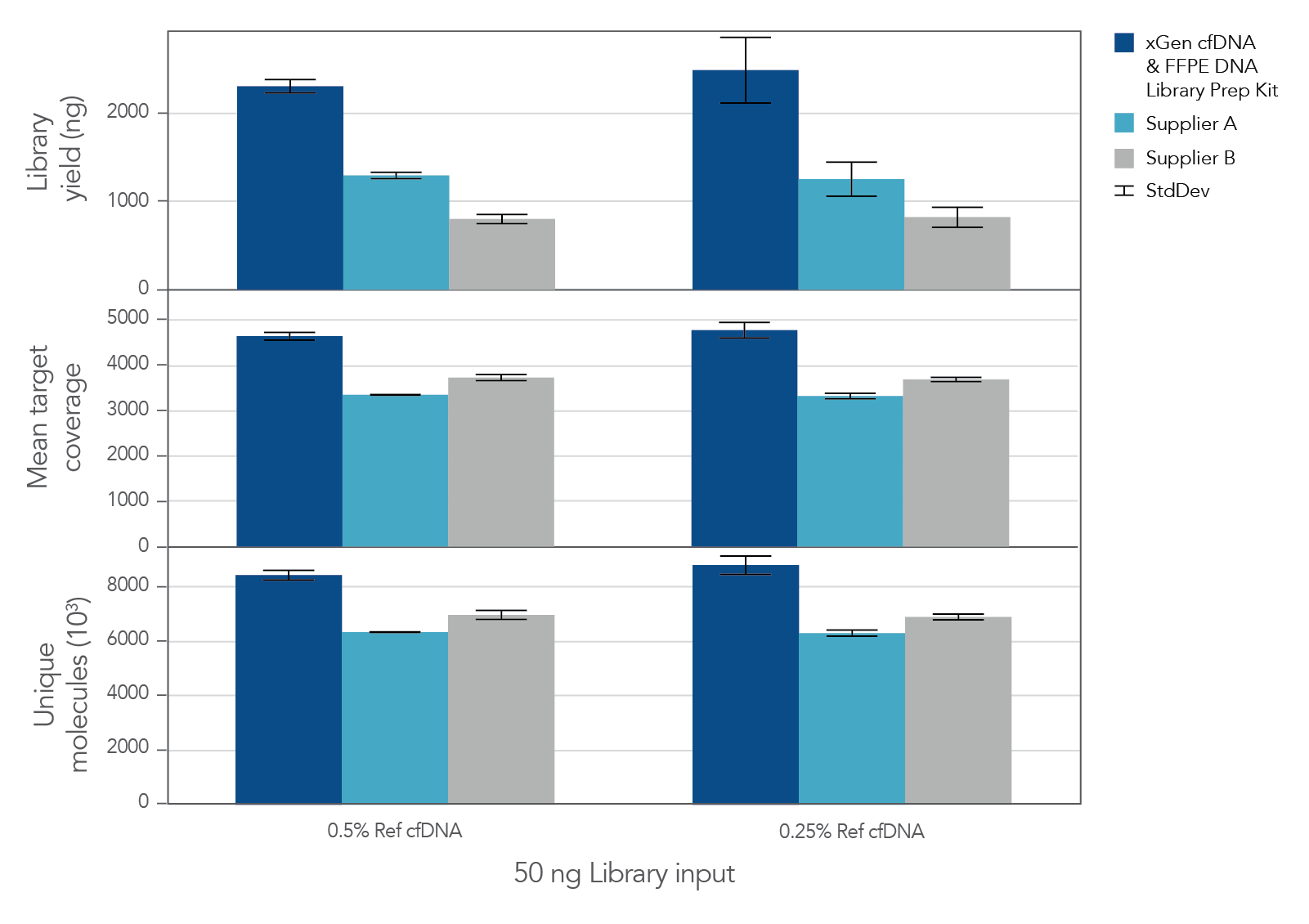
The unique, single-stranded ligation strategy of the IDT xGen cfDNA & FFPE DNA Library Prep v2 MC Kit and workflow delivers high conversion of input DNA molecules to sequencing data. This high conversion rate is critical for identification of ultra-low frequency variants, which is common in the analysis of cell-free DNA (cfDNA). A higher conversion rate translates to more complexity and coverage than other DNA library prep kits for cfDNA (Figure 3). In addition, the xGen cfDNA & FFPE DNA Library Prep Kit includes adapters that contain unique molecular identifiers (UMIs), which enable bioinformatic error correction. Combining higher complexity and coverage with stringent error correction better enables the identification of ultra-low frequency variants (Table 2).
Figure 3. xGen cfDNA &FFPE DNA Library Prep v2 MC Kit delivers higher yields, complexity, and coverage. Libraries were prepared in triplicate according to the manufacturer’s instructions with 50 ng of Horizon cfDNA reference standard and 7 cycles of PCR. Following quantification, libraries were captured with a custom 61 kb (target space) xGen Hyb Panel using the xGen Hybridization and Wash Kit. Captured libraries were pooled and sequenced on a NextSeq™ 500 (Illumina) using a high output 300 cycle kit and the manufacturer's protocol. After subsampling to 85M total reads, coverage and complexity were calculated.
Table 2. xGen cfDNA & FFPE DNA Library Prep Kit identifies low frequency variants in NGS reference samples
| Mutation | Expected VAF | xGen cfDNA & FFPE DNA Library Prep v2 MC Kit | Library Kit A | Library Kit B |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGFR: L858R | 0.25% | 0.13 (3/3) | 0.21 (3/3) | 0.21 (3/3) |
| EGFR: E746-A750 | 0.25% | 0.11 (3/3) | 0.19 (3/3) | 0.12 (3/3) |
| EGFR: T790M | 0.25% | 0.29 (3/3) | 0.36 (3/3) | 0.12 (3/3) |
| KRAS: G12D | 0.32% | 0.33 (3/3) | 0.36 (3/3) | 0.33 (3/3) |
| NRAS: Q61K | 0.32% | 0.23 (3/3) | 0.31 (2/3) | 0.22 (3/3) |
| NRAS: A59T | 0.32% | 0.17 (3/3) | 0.43 (2/3) | 0.22 (3/3) |
| PIK3CA:E545K | 0.32% | 0.16 (3/3) | 0.11 (3/3) | 0.36 (3/3) |
Table 2. Libraries were prepared in triplicate from 50 ng input Horizon cfDNA reference standards using the xGen cfDNA &FFPE DNA Library Prep v2 MC Kit in addition to two other commercially available library prep kits. Libraries were then captured with a custom 180 kb (target space) xGen Hyb Panel targeting 7 identified SNPs using the using the xGen Hybridization and Wash v2 Reagents and Beads. Captured libraries were pooled and sequenced on a NextSeq 500 (Illumina), using a high output 300 cycle kit and the manufacturer's protocol. After subsampling to 85M total reads, the average variant allele frequency for each of the targeted mutations was calculated for each library prep kits using VarDict.
Higher coverage and complexity deliver reliable variant and indel identification in FFPE samples
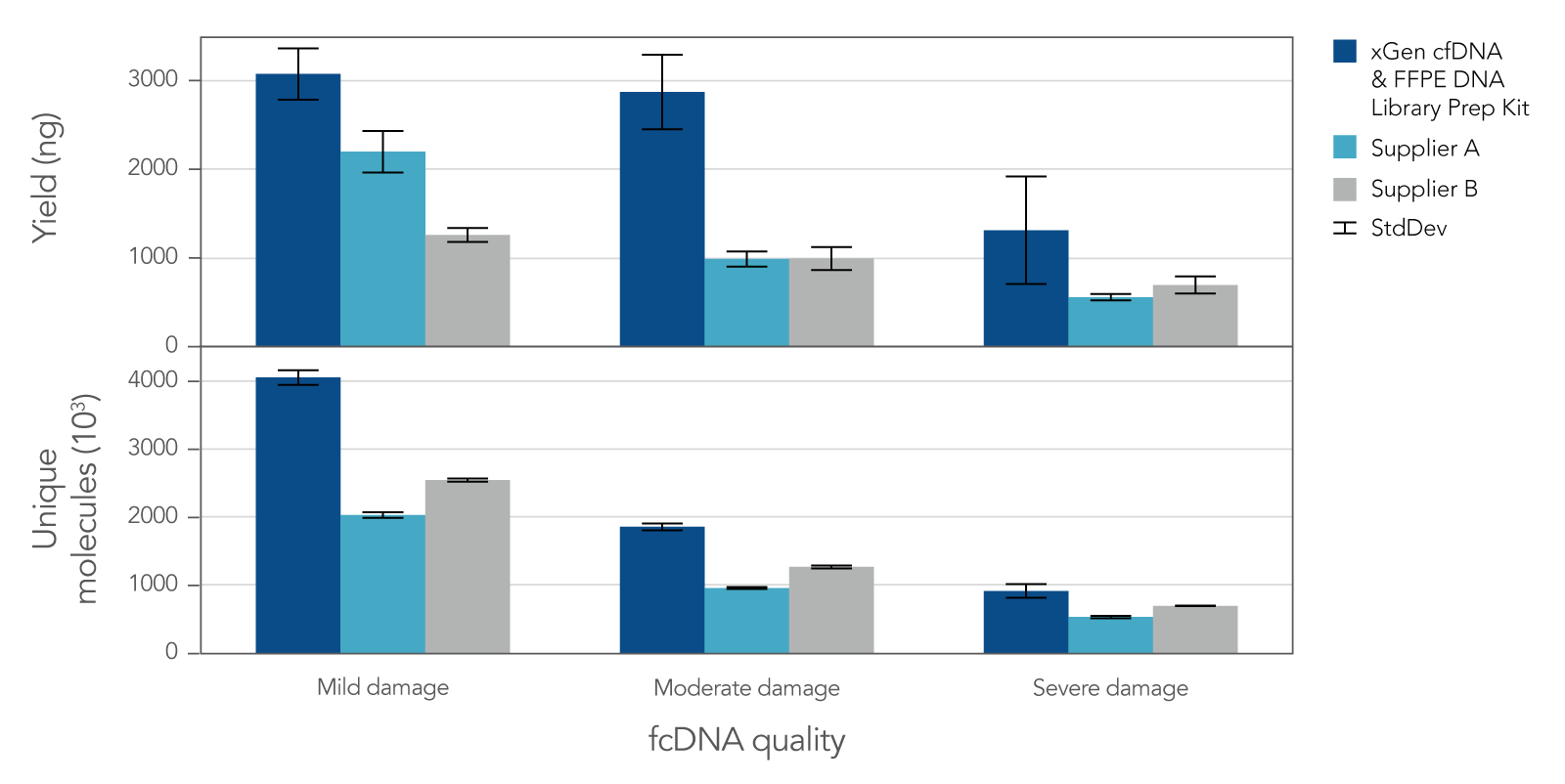
Research analysis of FFPE samples has its own unique challenges, including difficulties in generating libraries from samples of variable quality or with low inputs. The xGen cfDNA & FFPE DNA Library Prep v2 MC Kit leverages high conversion rates to achieve high library yields from low inputs of even severely damaged FFPE research samples (Figure 4). Higher conversion rates and yields translate to higher library complexity (Figure 4), which can increase confidence in variant calling. With severely damaged FFPE samples, the xGen cfDNA & FFPE DNA Library Prep v2 Kit delivers SNP and indel identification across a range of inputs (Table 3).
Figure 4. Library yield and complexity from varying qualities of Formalin Compromised DNA (fcDNA) reference standards. Libraries (n = 4 each) were prepared in triplicate by three commercial library prep kits following each of the manufacturer’s protocols with 25ng total input. Following 10 cycles of PCR, libraries were quantified using a Qubit™ dsDNA HS Kit. Then, 500 ng of each library were captured using a custom 180 kb (target space) xGen Hyb Panel with the xGen Hybridization and Wash v2 Reagents and Beads, following the xGen Hybridization and Wash Kit v2 protocol with an overnight hybridization and 13 cycles of PCR. The captured libraries were then pooled equimolar and sequenced on a NextSeq 500 (Illumina), using a high output 300 cycle kit and the manufacturer's protocol. Samples were subsampled to 8 million paired end reads and the number of unique molecules (HS library size) was determined with Picard.
Table 3. Observed Average Mutation Allelic Frequency of Severely Degraded FFPE DNA Library Input
| Variant | Expected VAF | 25ng | 50ng | 100ng | 250ng |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGFR: G719S | 24.5 | 23.9 (3/3) | 22.9 (3/3) | 22.1 (3/3) | 23.0 (3/3) |
| PIK3CA:H1047R | 17.5 | 16.9 (3/3) | 18.6 (3/3) | 17.5 (3/3) | 18.0 (3/3) |
| KRAS: G13D | 15.0 | 12.1 (3/3) | 13.2 (3/3) | 12.1 (3/3) | 12.0 (3/3) |
| NRAS: Q61K | 12.5 | 7.9 (3/3) | 11.3 (3/3) | 8.7 (3/3) | 8.9 (3/3) |
| BRAF: V600E | 10.5 | 11.2 (3/3) | 11.1 (3/3) | 11.0 (3/3) | 10.6 (3/3) |
| KIT: D816V | 10.0 | 8.0 (3/3) | 8.4 (3/3) | 7.7 (3/3) | 7.7 (3/3) |
| PIK3CA: E545K | 9.0 | 6.0 (3/3) | 7.0 (3/3) | 6.1 (3/3) | 6.3 (3/3) |
| KRAS: G12D | 6.0 | 5.7 (3/3) | 5.2 (3/3) | 6.3 (3/3) | 5.8 (3/3) |
| EGFR: L858R | 3.0 | 3.2 (3/3) | 2.9 (3/3) | 2.8 (3/3) | 2.5 (3/3) |
| EGFR: E746-A750 | 2.0 | 0.8 (3/3) | 0.5 (3/3) | 0.8 (3/3) | 0.5 (3/3) |
| EGFR: T790M | 1.0 | 0.9 (3/3) | 0.7 (3/3) | 0.8 (3/3) | 0.9 (3/3) |
Table 3. xGen cfDNA & FFPE DNA Library Prep v2 MC Kit enabled the mutation detection in severely degraded FFPE reference sample at varying library input. Each sample was captured with a custom 180 kb (target space) xGen Hyb panel targeting the verified mutations, using xGen Hybridization and Wash v2 Reagents and Beads, following the xGen Hybridization and Wash Kit v2 Protocol and sequenced to an average depth of 30 million read pairs on a NextSeq 500 (Illumina) using a high-output 300 cycle kit and the manufacturer's protocol. The average variant allele frequency (VAF) was calculated for each of the 11 mutations across all three replicates using VarDict, with a minimum variant allele depth of 3 single-stranded consensus reads. The number of replicates with a response is shown in parentheses.
Uniform GC coverage across the human genome
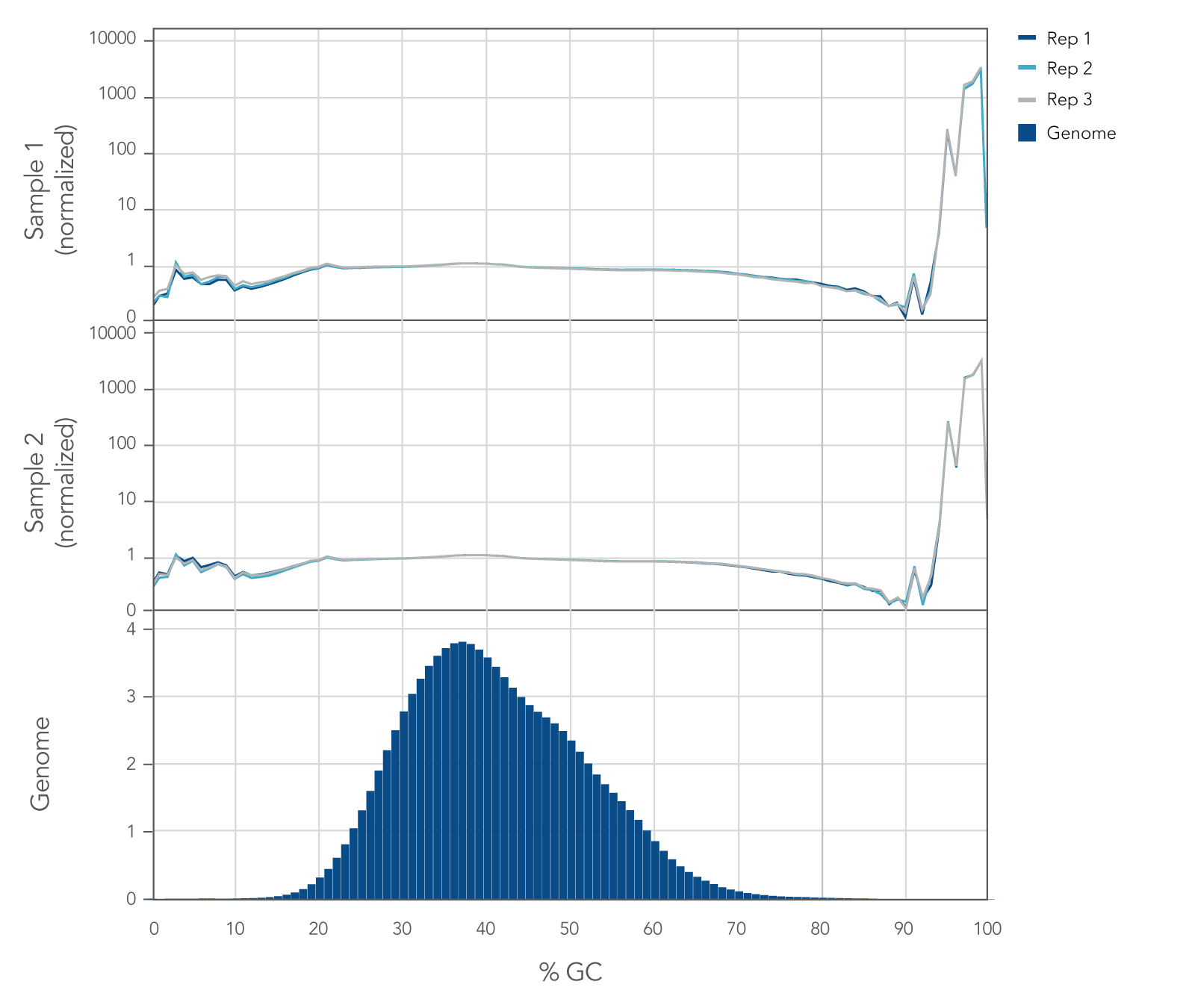
Internal whole genome sequencing (WGS) experiments demonstrated that the xGen cfDNA & FFPE DNA Library Prep v2 MC Kit has even coverage across the human genome with little evidence of bias (Figure 5), resulting in no significant GC bias for 99.7% of the human genome. Even coverage is made possible by the reduced number of PCR cycles required, due to higher conversion rates of input molecules.
Figure 5. xGen cfDNA & FFPE DNA Library Prep Kit normalized GC coverage across the human genome from cfDNA. 10ng cfDNA libraries were generated using xGen cfDNA & FFPE DNA Library Prep v2 MC Kit, using cfDNA extracted from two healthy donors from BioChain. Libraries were generated in triplicate using the manufacturer’s protocol, with 11 cycles of PCR. Libraries were quantified with Qubit dsDNA HS Kit and average size was determined with the Tapestation 4200 High Sensitivity D1000 (Agilent). Libraries were then pooled equimolar and sequenced on a Nextseq 500 (Illumina), using a high-output 300 cycle kit following the manufacturer’s protocol. The cfDNA libraries were subsampled to 20 million paired end reads for analysis with <0.2% of the genome bin at <15% GC and <0.1% of the genome bin at >80% GC.
Relative abundance of both ssDNA and dsDNA phage
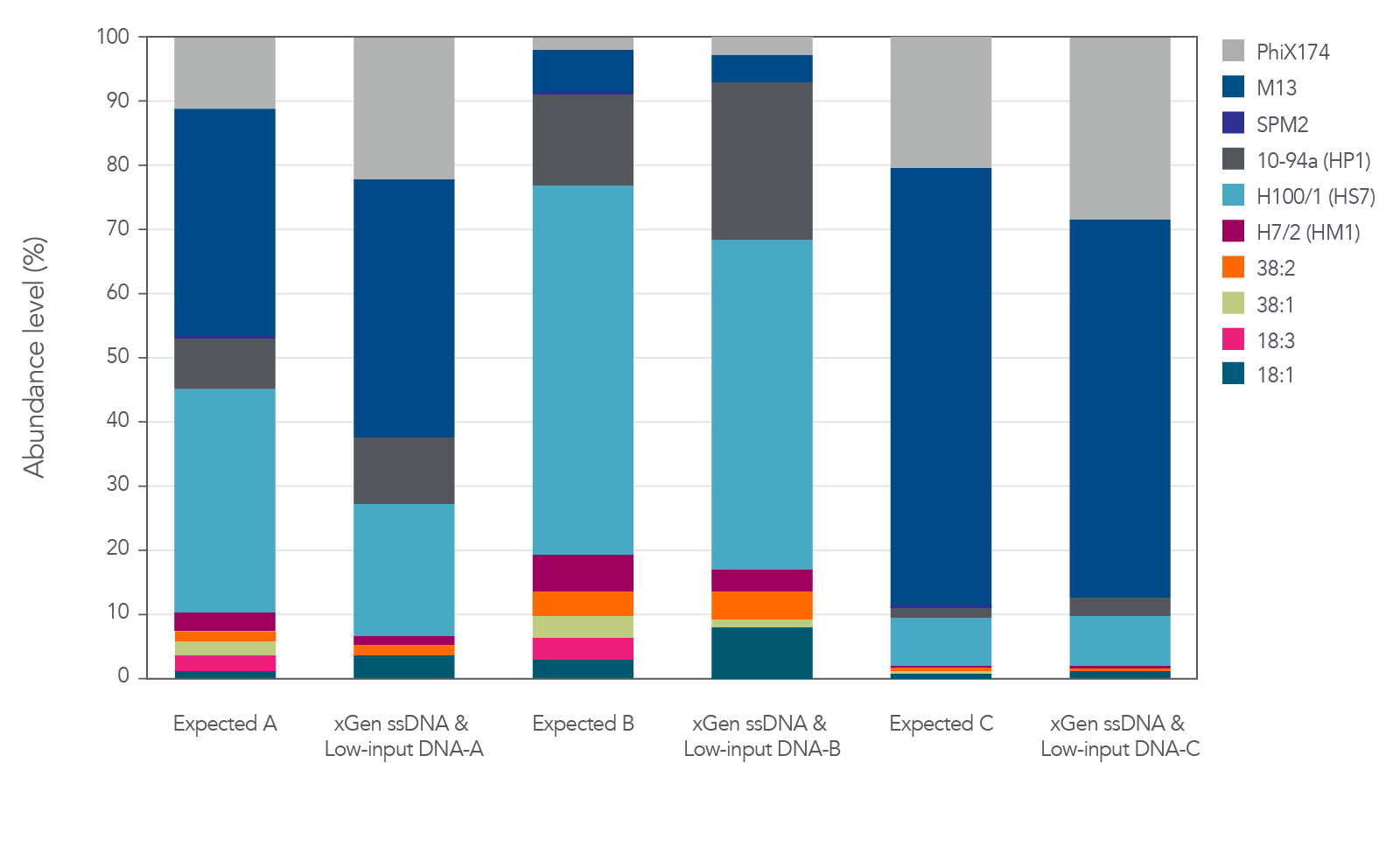
The xGen ssDNA & Low-Input DNA Library Prep Kit was used to prepare and sequence three artificial viromes containing different proportions of the ssDNA phage PhiX174 and M13 mixed with dsDNA phage (Figure 2). In this experiment, all cases supported that the proportions were preserved when sequenced with the xGen ssDNA & Low-Input DNA Library Prep Kit without any prior whole genome amplification for identification of ssDNA phage.
The libraries were sequenced on an Illumina® MiSeq® using v2 chemistry and 101 paired-end reads. Reads were then aligned with bowtie2 to assess the relative abundance of each virus, defined as the number of reads mapped normalized by genome size. These virome abundance values were then compared to the copy number of each genome in the AVC, estimated through SYBR® Green counts for the dsDNA phages, or calculated based on the quantity of DNA measured with NanoDrop® (Thermo Fisher) readings for ssDNA phages. The expected abundance of dsDNA phages was doubled to correct for the presence of two DNA molecules that can act as potential templates compared to a single potential template for ssDNA viruses.
Figure 2. Libraries developed from mixtures of ssDNA and dsDNA phage. Three artificial viral communities (AVCs) were prepared by mixing the isolated gDNA from two ssDNA phages (M13 and PhiX174) with gDNA isolated from eight dsDNA phages (SPM2, 10-94a, H100/1, H7/2, 38:2, 38:1, 18:3, and 18:1) at different ratios of ssDNA to dsDNA. Artificial viral community A contained 50% ssDNA and 50% dsDNA phage, AVC B contained 10% ssDNA and 90% dsDNA phage, and AVC C contained 90% ssDNA and 10% dsDNA phage. The AVCs were sheared to 200 bp using an M220 Covaris® instrument according to the manufacturer’s instructions, and NGS libraries were constructed utilizing the xGen ssDNA & Low-Input DNA Library Prep Kit.
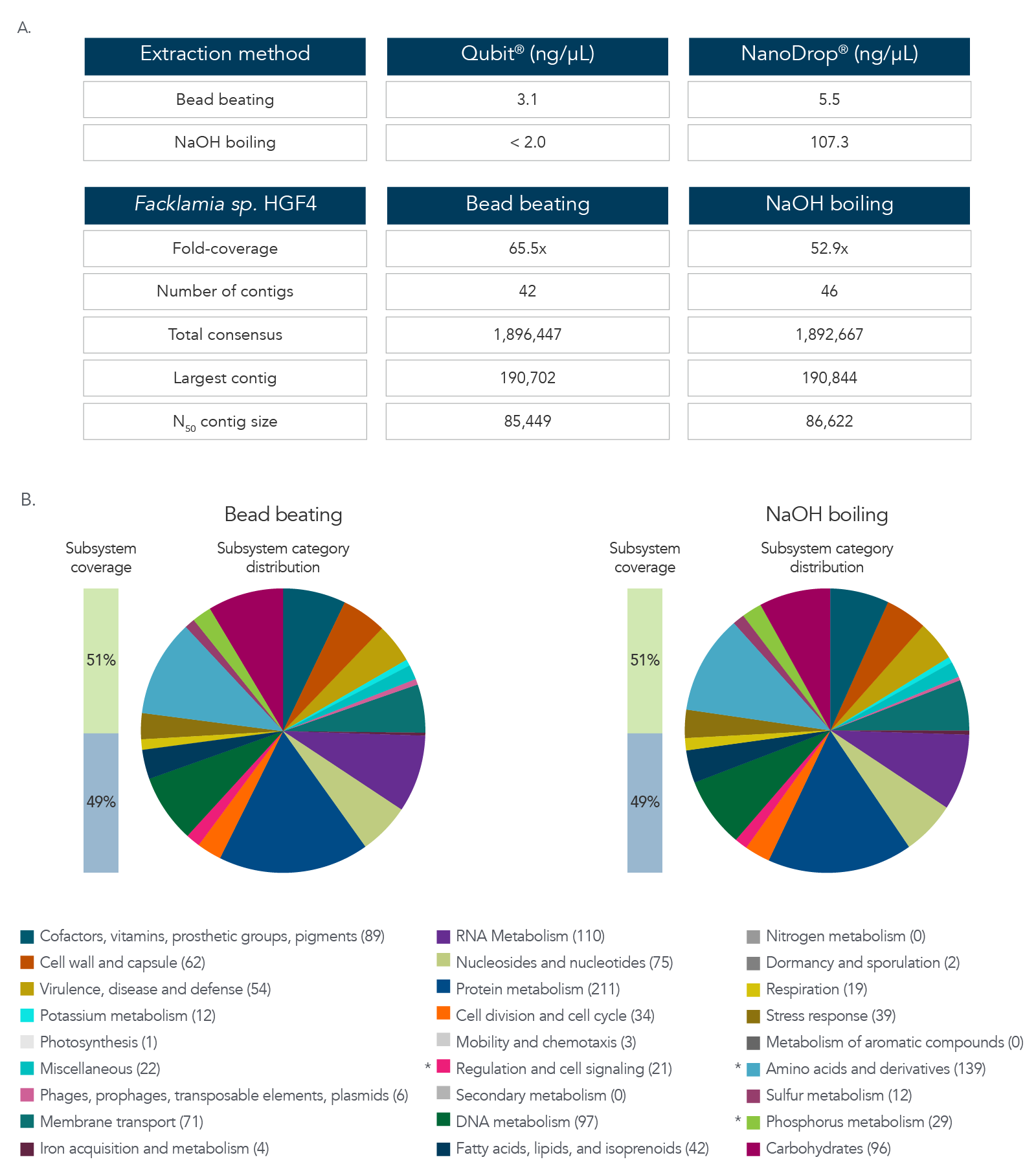
DNA extraction and sequencing of a hard-to-extract microbe
The data in Figure 3A and B show results after DNA extraction and sequencing of Facklamia sp., a microbe recognized for the difficulty it presents for DNA extraction. Pure cultures of Facklamia sp. HGF4 were grown up to 2 x 109 CFU/mL. Facklamia sp. HGF4 was selected because it is a Gram-positive isolate with gDNA that is difficult to extract using a nondenaturing bead-beating extraction method. Because Facklamia sp. HGF4 does not have a reference genome, de novo assembly of the sequencing output was required. Bacterial culture was split into two aliquots—one from which gDNA was isolated using bead beating, and one from which the gDNA was extracted by denaturing NaOH boiling. Briefly, 1 mL of 2 x 109 CFU/ml bacteria was pelleted by centrifugation, the supernatant was removed, and cells were resuspended in 50 µL of sterile water. Then, 50 µL of 0.1 N NaOH was added to the bacterial suspension, and the sample was mixed by vortexing and then boiled at 95 °C for 15 minutes. The solution was then chilled on ice and neutralized by adding 8 µL of Tris-HCl, pH 7.0. The sample was centrifuged at 15,000 x g for two minutes to pellet the cell debris and any unlysed cells, and the supernatant was transferred to a new reaction tube. The isolated gDNA was precipitated with isopropanol to clean and concentrate the sample. DNA recovery was quantified by Qubit® (Thermo Fisher) for dsDNA and NanoDrop for ssDNA. Libraries were prepared using the xGen ssDNA & Low-Input DNA Library Prep Kit. Facklamia sp. HGF4 was assembled de novo using MIRA 4.0 and annotated using the RAST server.
Figure 3. DNA extraction and sequencing of a hard-to-extract microbe. (A) DNA extraction by NaOH boiling produced higher DNA yields from Facklamia sp. than bead beating, and in less time. (B) Sequencing of the NaOH-extracted DNA produced a comprehensive, de novo assembled genome sequence that was indistinguishable from that produced from bead-beating extracted DNA.
Low input and PCR-free workflows
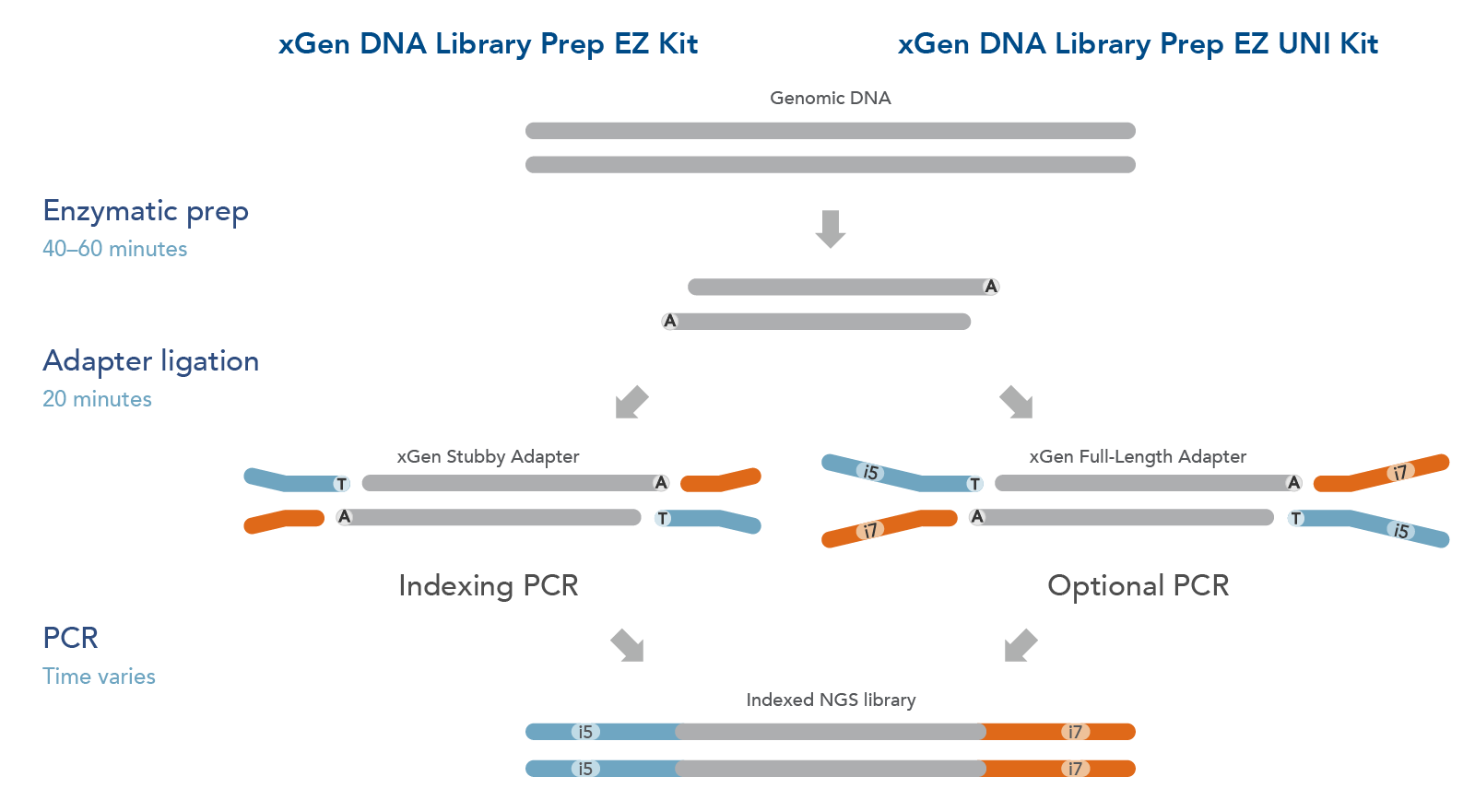
The xGen DNA Library EZ Kits are available in two configurations (Figure 1): xGen DNA Library EZ kit (Standard kit) and xGen DNA Library EZ UNI kit (Universal kit).
- The xGen DNA Library EZ kit supports indexing by PCR workflow, it includes xGen Stubby Adapters. Indexing primers are supplied separately.
- The xGen DNA Library EZ UNI kit supports an indexing by ligation workflow for optional PCR amplification or PCR-free workflow, amplification primers are included in the kit. Indexed adapters are supplied separately.
Both kits include an enzymatic fragmentation module, a high efficiency ligase, and a PCR Master Mix that can generate library yields sufficient for hybridization-based enrichment or direct sequencing. Both kits have workflows compatible with high throughput applications and have been automated on multiple liquid handlers.
Figure 1. Workflow for the xGen DNA Library Prep EZ Kits. xGen DNA Library Prep EZ Kits are compatible with either an indexing by PCR workflow using xGen Stubby Adapters included in the kit and indexing primers supplied separately (left) or an indexing by ligation workflow using full length, indexed Y adapters (right). Both kits include amplification reagents for Indexing PCR or optional PCR amplification.
Table 1. Supported applications
| Research applications | xGen DNA Library EZ Kit and EZ UNI Kit |
|---|---|
| Whole genome sequencing | ✓ |
| Whole exome sequencing | ✓ |
| Variant detection | Germline + somatic |
| Genotyping | ✓ |
| CNV detection | ✓ |
Table 2. Specifications
| Features | xGen DNA Library EZ Kit | xGen DNA Library EZ UNI Kit |
|---|---|---|
| Sample types | Fresh frozen tissue, genomic DNA, PCR amplicons, high quality FFPE* | |
| Range of input concentrations | 0.1–1000 ng | 0.1–1000 ng |
| Indexing compatibility | CDI primers up to 96-plex, compatible with xGen Normalase Module UDI primers up to 1536-plex, compatible with xGen Normalase Module | xGen indexing primers for custom, full-length and truncated adapters, compatible with xGen Normalase Module |
| System compatibility and multiplexing format | Illumina® sequencing instruments compatibility | Manual and automated. Please inquire for a list of compatible liquid handling robots and scripts. |
*Optimization of the enzymatic fragmentation step may be required.
xGen Deceleration Module enables additional control over fragment length with the xGen DNA Library EZ Kits.
The xGen Deceleration Module
- generates an average library insert size of 550 bp
- offers flexible fragmentation times on automation platforms
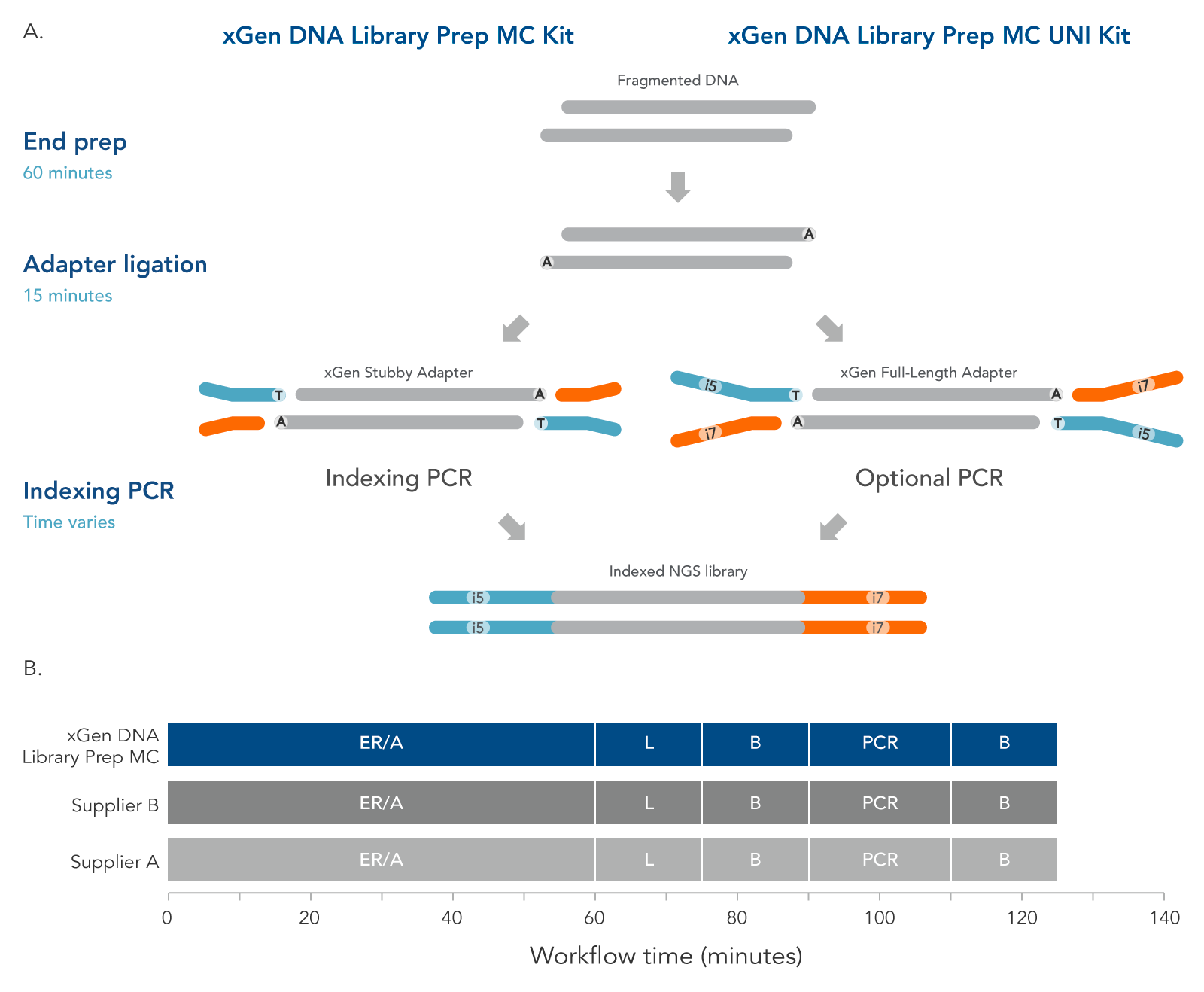
The xGen DNA Library Prep MC Kits offer a versatile solution to streamline dsDNA, NGS sample preparation for Illumina® sequencing platforms. This workflow processes fragmented DNA, such as Covaris®-sheared DNA, for rapid and efficient end repair, adenylation, and adapter ligation. It includes an optional library amplification step, thus enabling both manual and automated workflows. These kits can also be used for targeted hybridization capture. The HiFi Polymerase Master Mix, which is supplied in the kit, is suitable for pre-hyb PCR to produce yields of 500 ng or more from as little as 1 ng DNA input. These kits are also compatible with any of the predesigned xGen Hyb Panels or a xGen Custom Hyb Panel.
Table 5. Specifications
| Feature | xGen DNA Library MC Kit | xGen DNA Library MC UNI Kit |
|---|---|---|
| Sample types | Genomic DNA extracted from tissue, blood, microbial isolates, and environmental samples | |
| Input concentration and type | 1 ng–1 µg input DNA in 50 µL volume | |
| Indexing compatibility | CDI primers up to 96-plex and UDI primers up to 1536-plex | xGen indexing primers for custom full-length and truncated adapters |
| System compatibility and multiplexing format | Illumina® sequencing instruments | |
| Workflow compatibility | Manual and automated. Please inquire for a list of compatible liquid handling robots and scripts. | |
Rapid, flexible workflow
The xGen DNA Library Prep MC protocol (Figure 4) contains two enzymatic incubations, an indexing or optional PCR, and bead-purification steps. The protocol minimizes sample handling, shortening the overall, library preparation time to two hours with PCR.
Figure 3. Workflow for the xGen DNA Library Prep MC Kits. These kits are available in two configurations to support two indexing workflows. The incubation steps consist of end repair, polishing of dsDNA, and A-tailing, all performed in a single End Prep reaction followed by ligation of either a stubby Y adapter (xGen DNA Library Prep MC kit, left) or full-length indexed Y adapter (xGen DNA Library Prep MC UNI Kit, right). The xGen DNA Library Prep MC workflow incorporates an indexing PCR step after adapter ligation to complete the adapter sequences. PCR is an optional step for the MC UNI Kit. xGen DNA Library Prep MC Kits are compatible with various indexing primers and full-length indexed Y adapters, including UDI and UMI adapters and up to 1536 UDI primer pairs. Both kits are compatible with the Normalase module. The xGen DNA Library Prep MC workflow is comparable to other kit suppliers, where a 60-minute end repair/A-tailing step (ER/A) is followed by a 15-minute adapter ligation step (L), a bead-based purification (B), an optional library amplification step (PCR), and a second, bead-based purification (B).
Applications
The xGen cfDNA & FFPE DNA Library Prep MC Kit v2 produces next generation sequencing (NGS) libraries suitable for many research applications that use degraded samples, including:
- Low-frequency, somatic variant identification of SNPs
- Insertions/deletions (indels)
- Identification of inherited germline SNPs and indels
- Whole genome sequencing (WGS)
The xGen cfDNA & FFPE DNA Library Prep protocol takes about 4 hours and includes only four major steps, minimizing sample handling (Figure 1):
- End repair. The End Repair Enzyme Mix converts cfDNA, or sheared, input DNA such as FFPE DNA into blunt-ended DNA that is ready for ligation.
- Ligation 1. The Ligation 1 Enzyme catalyzes the single-stranded addition of the Ligation 1 Adapter to only the 3′ end of the insert. This novel enzyme is unable to ligate inserts together, minimizing the formation of chimeras. The 3′ end of the Ligation 1 Adapter also contains a blocking group to prevent adapter-dimer formation.
- Ligation 2. The Ligation 2 Adapter acts as a primer to gap-fill the bases complementary to the Ligation 1 Adapter, followed by ligation to the 5′ end of the DNA insert to create a double-stranded product.
- PCR amplification. The xGen 2x HiFi PCR Mix is included to perform indexing PCR (primers sold separately) for Illumina® sequencing.
Figure 1. Workflow for the xGen cfDNA & FFPE DNA Library Prep v2 MC Kit. In an initial step, end repair enzymes convert cfDNA, or sheared, input DNA into blunt-ended DNA ready for ligation. Then, a Ligation 1 Enzyme catalyzes the single-stranded addition of a Ligation 1 Adapter to the 3′ end of the insert. This novel enzyme is unable to ligate inserts together which minimizes chimera formation. The 3′ end of the Ligation 1 Adapter also contains a blocking group to prevent adapter-dimer formation. The Ligation 2 Adapter acts as a primer to gap-fill bases complementary to the Ligation 1 Adapter, followed by ligation to the 5′ end of the DNA insert which creates a double-stranded product. In a final step, PCR with the IDT 2x HiFi PCR mix incorporates sample index sequences for sequencing on Illumina® platforms.
Technical Details
The xGen cfDNA & FFPE DNA Library Prep v2 MC Kit includes all the reagents required for End Repair, Ligation 1 and Ligation 2 reactions, and PCR.
Table 1. Specifications, additional reagents, and equipment.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Sample types | High-quality DNA, cfDNA, DNA from FFPE samples |
| Input range | 1–250 ng |
| Adapters | Included |
| Indexing primers (not included) | xGen UDI Primers* |
| PCR amplification reagents | xGen 2x HiFi PCR Mix, included |
| Compatible sequencing platforms | Illumina® sequencing instruments |
| Compatible hybrid capture blockers | xGen Universal Blockers—TS Mix |
*Contact us for immediate assistance in ordering other indexing designs or configurations.
Complete workflow for hybridization capture research experiments
The xGen cfDNA & FFPE DNA Library Prep v2 MC Kit was designed to work seamlessly with xGen hybridization capture probes and reagents (Figure 2). Whether your project requires whole exome sequencing or custom panels, IDT has the capture solutions for you.
NGS DNA library construction from samples with damaged DNA
The xGen ssDNA & Low-Input DNA Library Prep Kit enables library preparation from damaged samples that can be difficult to obtain sequence information. The xGen ssDNA & Low-Input DNA Library Prep Kit can create libraries in 2 hours from as little as 10 pg of input material. Libraries can be prepared from heavily damaged samples by using IDT Adaptase technology. Unlike other library methods, the Adaptase technology generates library molecules from single-stranded DNA fragments, which allows better recovery of sample input DNA complexity from heavily nicked and degraded samples compared to other commercially available products for Illumina® platforms. Sample types include degraded FFPE, ancient DNA, chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), and other enriched samples that have undergone DNA damage.
Rescue valuable sequencing data from low-abundance samples with ssDNA content
The xGen ssDNA & Low-Input DNA Library Prep Kit is designed for users needing to sequence samples containing ssDNA for research. These include metagenomic and viromic samples where relative abundance of both ssDNA and dsDNA phage and viral genomes can be identified. Other compatible sample types include heat-denatured pathogenic samples, samples extracted under harsh denaturing conditions to decrease extraction bias, and oncology-related liquid biopsy samples when detection of single-stranded cfDNA content is desired.
Workflow
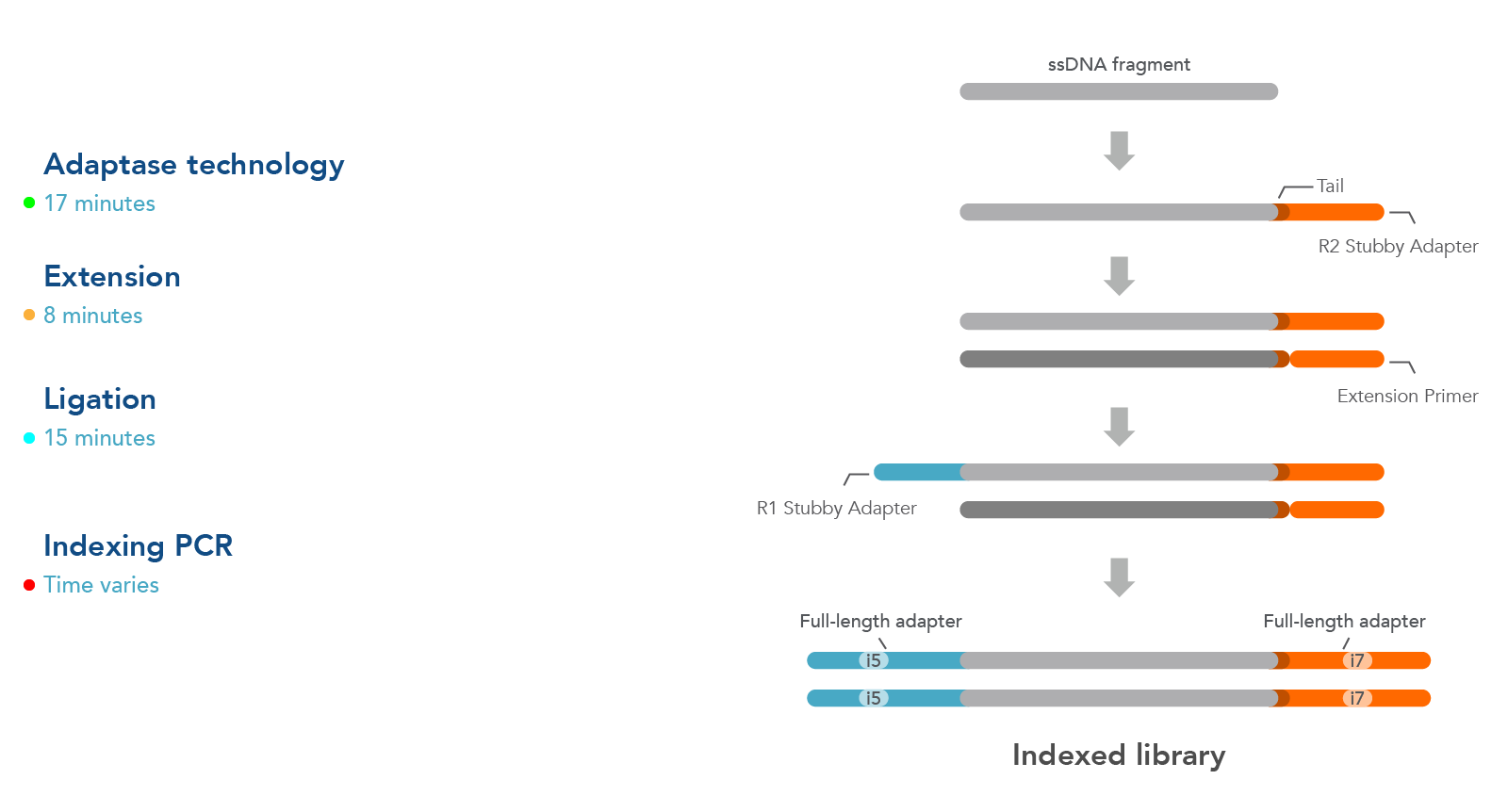
The workflow for this kit is shown in Figure 1. As illustrated in this diagram, samples undergo four steps:
- Adaptase technology—the Adaptase reaction simultaneously performs tailing and ligation of R2 Stubby Adapter to the 3´ ends in a highly efficient, template-independent manner.
- Extension—the extension reaction generates a second strand prior to ligation.
- Ligation—ligation reaction adds R1 Stubby Adapter to the original strand.
- Indexing PCR—PCR is used to incorporate sample indexes and sequences needed for Illumina® sequencing. Indexing primers are supplied separately.
Figure 1. Workflow used for the xGen ssDNA & Low-Input DNA Library Prep Kit. Four steps are followed as described in the text.
Specifications
| Feature | xGen ssDNA & Low-Input DNA Library Prep Kit |
|---|---|
| Sample types | Low-quality degraded DNA, ssDNA, mixtures of ssDNA and dsDNA |
| Input amount | 10 pg to 250 ng |
| Indexing compatibility | CDI primers up to 96-plex UDI primers up to 1536-plex |
| System compatibility and multiplexing format | Illumina® sequencing instruments |
| Workflow compatibility | Manual & automated. For list of liquid handlers and scripts, please inquire. |
xGen™ DNA EZ Library Prep Kit
Double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) library prep for enzymatic fragmentation. Includes library prep and polymerase for amplification. Available in two configurations: The xGen™ DNA Library Prep EZ Kits include xGen™ Stubby Y Adapters for indexing by PCR workflows (indexing primers must be purchased separately). The xGen™ DNA Library EZ UNI Kit requires the purchase of full-length, indexed adapters for PCR-free indexing by ligation workflow.
xGen™ UDI-UMI Adapters
Full-length adapters with unique dual indexes and optional unique molecular identifiers for sensitive NGS applications. Utilizes TA ligation workflow for incorporating sample indexes during the ligation step.
xGen™ Normalase Module and Indexing Primers
Use our xGen Normalase Module with the xGen Normalase UDI Primers to allow for quick and easy library normalization and pooling for sequencing. Each plate of xGen™ Normalase UDI Primers contains 96 barcoded primer pairs.
xGen™ UDI Primer Pairs (subset)
Premixed unique dual index primer pairs for sample indexing by PCR. These are delivered as single-use plates containing either 16, 96 (Plate 1), or 384 primer pairs (Plates 1-4).
xGen™ Deceleration Module
Single reagent used during enzymatic fragmentation with the xGen™ DNA Library Prep Kit EZ, it enables larger 550 bp insert size and room temperature setup on automation platforms (deceleration = slower fragmentation).
xGen™ DNA MC Library Prep Kit
Double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) Library prep for mechanically fragmented DNA. Includes library prep and polymerase for amplification. Available in two configurations: The xGen™ DNA Library Prep MC Kits include xGen™ Stubby Y Adapters for indexing by PCR workflow (indexing primers must be purchased separately). The xGen™ DNA Library MC UNI Kit requires the purchase of full-length, indexed adapters for PCR-free indexing by ligation workflow.
xGen™ cfDNA & FFPE DNA Library Prep v2 MC Kit
High conversion DNA library prep kit for analysis of cfDNA and FFPE, supporting mechanically (MC) sheared inputs when shearing is needed on FFPE samples. This v2 kit includes IDT's internally-developed xGen 2x HiFi PCR Mix, for a complete library prep solution.
xGen™ Input DNA Quantification Primers
Two primer pairs to human ALU repeat sequences to determine usable input DNA, assesses DNA quantity and integrity with ratio of 115/247 bp amplicons; comprises primer pairs only; qPCR Master Mix sourced separately (separate vendor).
xGen™ ssDNA & Low-Input DNA Library Prep Kit
Library prep kit for ssDNA (heavily damaged) or mixtures of ss and dsDNA (viromes/metagenomes) from 10 pg–250 ng; Adaptase™-based chemistry for library prep of single stranded DNA, includes amplification polymerase; indexing primers also supplied separately.
xGen™ Normalase™ CDI Primers
Combinatorial dual index primers designed for Normalase workflow. Consists of 20 individual tubes of indexes that support up to 96 combinations of i7-i5 indexes.
Legacy Swift Indexing Primers
Legacy Swift Primers, CDI and UDI indexing strategies. The xGen™ CDI Primers are individual tubes of indexes, to be arrayed in a combinatorial fashion for up to 96 possible barcode combinations, and the xGen™ UDI Primers, Plate 2 are premixed Unique Dual Index primers in single-use plates. Both products have 8nt barcodes. Note that these primers are not compatible with any other IDT indexing primers, due to potential demultiplexing issues.
xGen™ Normalase™ UDI Primers
Premixed, unique dual index primers designed for Normalase™ workflow. Individual plates of 96 indexes or sets of 384 indexes are available. Or choose all four sets for a total of 1536 index pairs. All plates are single-use to minimize the risk of contamination by multiple handling events.
xGen™ UDI Primer Pairs
Premixed unique dual index primer pairs for sample indexing by PCR. These are delivered as single-use plates containing either 16 or 96 primer pairs, or for high-volume/high-throughput customers we have bulk 2 nmol offerings of primer with 10 nt indexes. The 10 nt indexes are available in sets of 384, 768, and 1536 index pairs. All plates except the bulk 2 nmol offerings are single-use to minimize the risk of contamination by multiple handling events.
xGen DNA Library Prep EZ Kit and xGen DNA Library Prep EZ UNI Kit Protokoll
xGen DNA Library Prep MC Kit and xGen DNA Library Prep MC UNI Kit Protokoll
xGen Normalase Module Protokoll
xGen Deceleration Module Protokoll
xGen cfDNA & FFPE DNA Library Prep v2 MC Kit ismertető
xGen cfDNA and FFPE DNA Library Prep v2 MC Kit Protokoll
xGen ssDNA and Low-Input DNA Library Prep Kit Protokoll
 Forgalmazott termékeink gyártói - keressen gyártó szerint a logóra kattintva
Forgalmazott termékeink gyártói - keressen gyártó szerint a logóra kattintva