This fast and automatable workflow improves cluster density and library balance and can easily be integrated into your standard DNA and RNA library preparation protocols for research studies to increase efficiency and reduce cost for NGS research laboratories.
xGen™ NGS—made to streamline.
IDT termékek szállítási költségei 2024.04.-től:
A szintézis helyétől, valamint a szállítási körülményektől függően az alábbi költségek kerülnek felszámításra:
-
Belgiumból: nettó 6 900 Ft
USA-ból: nettó 34 000 Ft
Belgiumból, szárazjégen: nettó 37 000 Ft
USA-ból, szárazjégen: nettó 45 000 Ft
- Oldatok szállítási költsége: mennyiség és súly függvénye, kérjen ajánlatot a Bio-Science Kft.-től!
Általános tájékoztató az IDT USA gyártási központjából érkező „custom” termékcsoportokról:
szintetikus biológiai termékek:
- Gének
- gBlocks, eBlocks
- Ultramerek
- RNS-oligók
- CRISPR guide RNS-ek
- oPools
qPCR próbák:
a szintézis helye a szekvencia komplexitásától, valamint a választott festék/ quencher kombinációtól függ
szolgáltatások:
- PAGE tisztított termékek
stock termékek:
nem áll teljes lista rendelkezésre, kérjen ajánlatot a Bio-Science Kft.-től!
The xGen Normalase Module offers a novel enzymatic library normalization technology that consolidates DNA or RNA library normalization and pooling for loading on Illumina® systems in research studies. The Normalase workflow eliminates the need for library concentration adjustment prior to library pooling, improving cluster density and library balance.
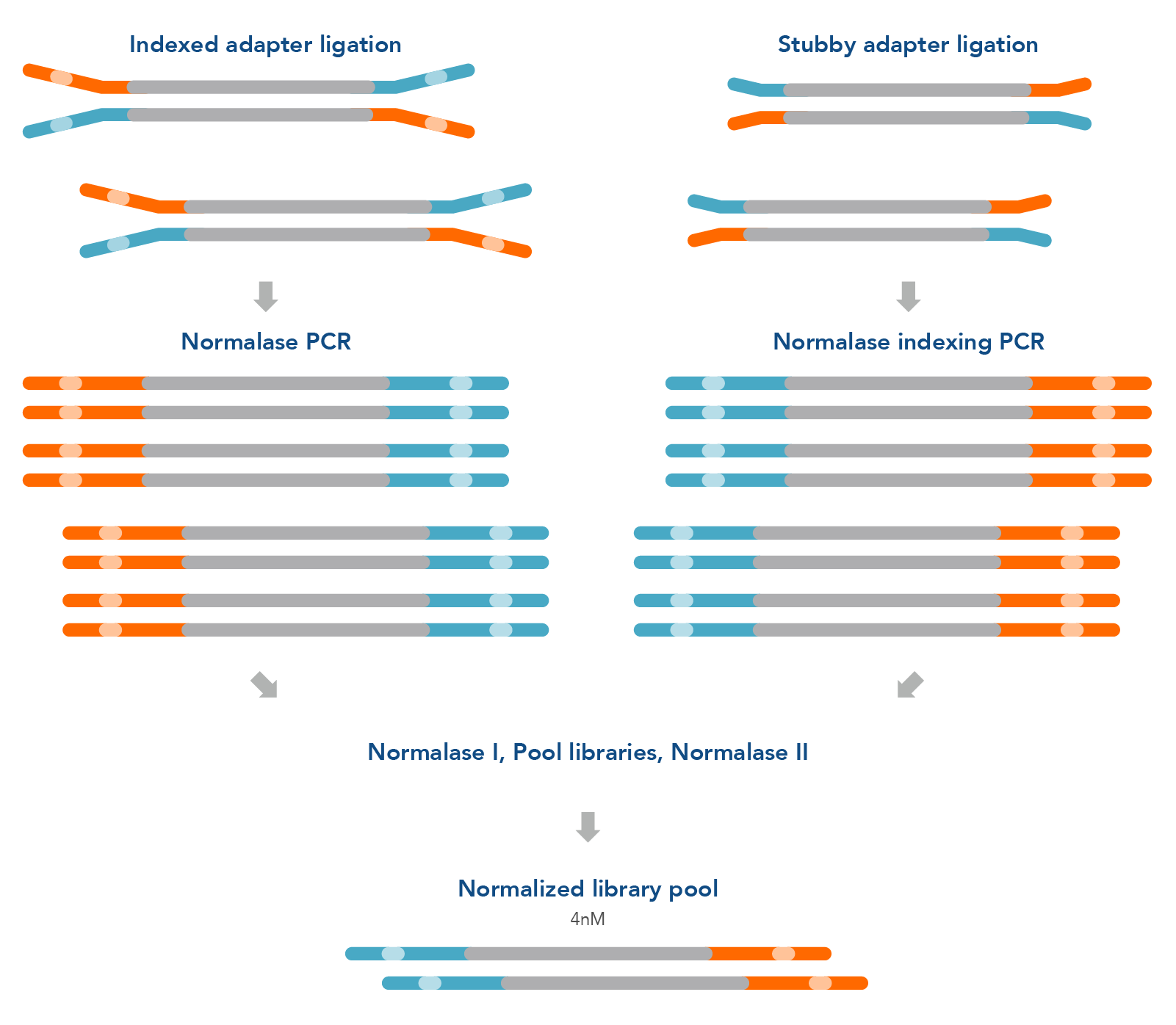
The xGen normalization method can easily be integrated into standard library preparation protocols to improve turnaround time and loading accuracy for NGS laboratories. The library selection and enzymatic normalization steps of the Normalase workflow (Figure 1) are designed for research workflows that consistently produce amplified library yields 3x the target normalization amount following library amplification with Normalase primers. For example, ≥6 nM or ≥12 nM yield in 20 μl volume achieves 2 nM or 4 nM normalized library yield; a ≥6 nM normalization workflow will result in a 2 nM final normalized library pool, which can be concentrated to achieve 4 nM.
This workflow does not introduce a second PCR; instead, it replaces the primers in conventional library amplification, either terminal or indexing. The xGen Normalase Kits offer a fast, scalable library normalization workflow for high-throughput research laboratories.
Figure 1. Normalase research workflow. The xGen Normalase research workflow begins after NGS library adapter ligation, using either full-length indexed adapters or truncated adapters, where Normalase PCR primers are used to amplify the libraries to above the minimum threshold and condition the libraries for downstream Normalase enzymology. For full-length indexed adapter libraries, xGen Normalase terminal primers are used; for truncated adapter libraries, xGen Combinatorial Dual Indexing Normalase primers are used. Amplified and conditioned NGS libraries are then individually incubated for 15 minutes with the Normalase I Master Mix to enzymatically select a specified molarity of each NGS library. After Normalase I, each library is pooled using equal volumes into a single tube and incubated for 15 minutes with the Normalase II Master Mix which enzymatically normalizes each NGS library to the specified selected molarity. The result of Normalase is a balanced, multiplexed NGS library pool ready for sequencing.
** ≥6 nM normalization workflow will result in a 2 nM final normalized library pool, which can be concentrated to achieve 4 nM. **
For research use only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Unless otherwise agreed to in writing, IDT does not intend for these products to be used in clinical applications and does not warrant their fitness or suitability for any clinical diagnostic use. Purchaser is solely responsible for all decisions regarding the use of these products and any associated regulatory or legal obligations.
Consistent DNA library normalization and reliable results across variable insert sizes
| Loading (pM) | Cluster density (K/mm2) | # of libraries | Library balance (CV%) | Insert size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 1370 | 6 | 9.7 | 150 |
| 12 | 1043 | 16 | 8.2 | 200 |
| 12 | 1157 | 6 | 5.4 | 350 |
| 12 | 1070 | 5 | 3.7 | 600 |
Table 1. Expected and consistent cluster density generation using MiSeq® V2 chemistry at 12 pM from library pools normalized to 4 nM using Normalase.
Better normalization compared to conventional methods
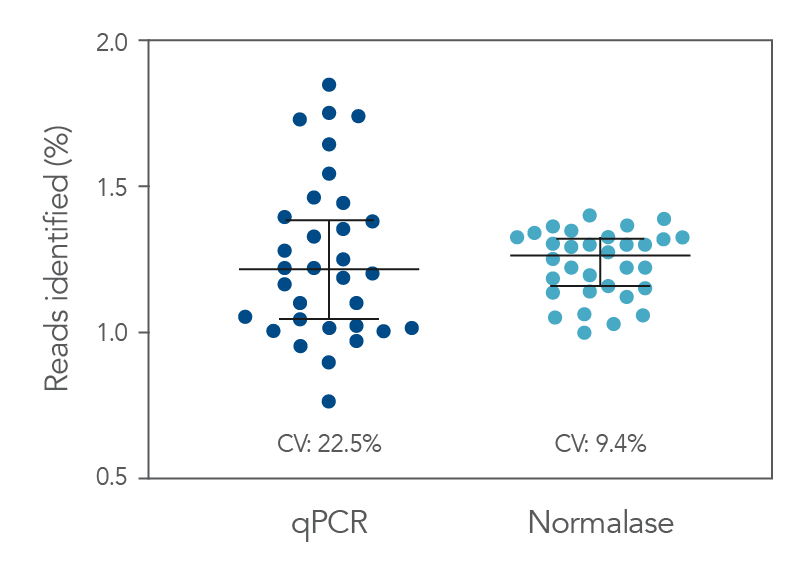
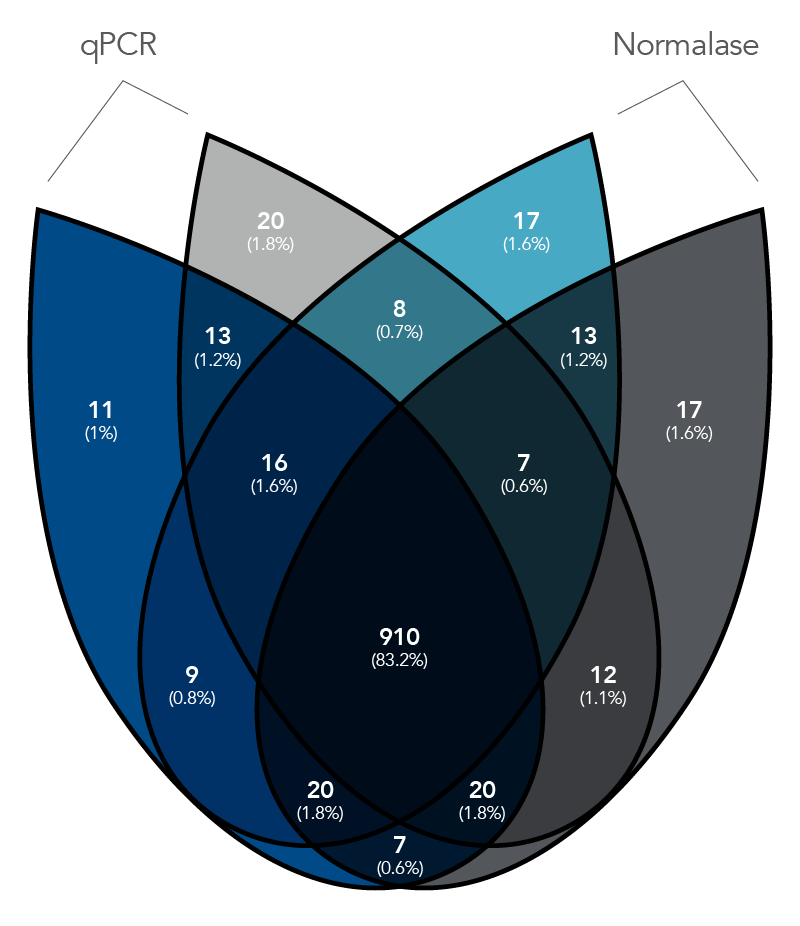
Figure 2. qPCR vs. Normalase. Thirty-two xGen DNA libraries were generated with full-length indexed adapters between two users (n=16/user) with 1-250 ng inputs of NA12878 gDNA. Post-Normalase PCR libraries were quantified with qPCR assuring the libraries met the minimum threshold. Libraries were either normalized and pooled and sequenced based on the qPCR quant or, using the same libraries, pooled and normalized using Normalase and sequenced to determine percent Reads Identified of each index (MiSeq V2 50 cycle Nano). The coefficient of variation (CV) for the qPCR pool was 22.5% across the two users, while the CV for the Normalase pool was 9.4%. Lines are median and 95% confidence interval.
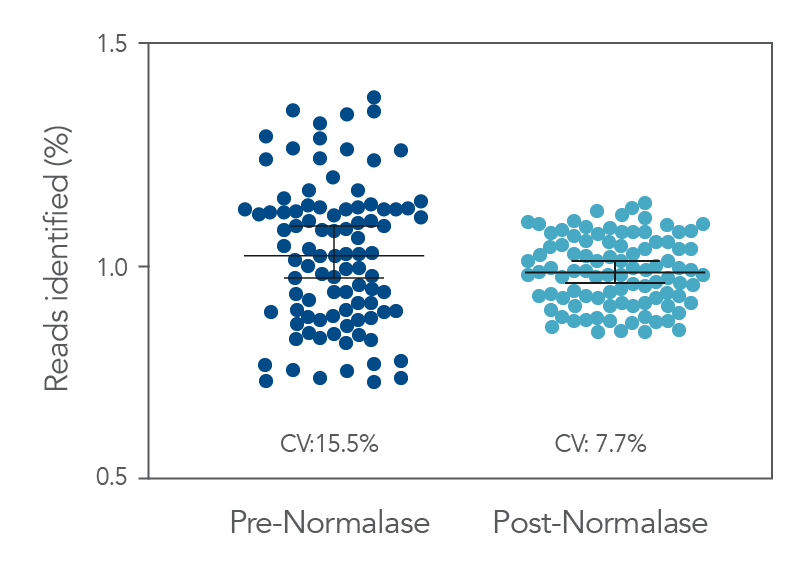
Figure 3. Pre- vs. Post-Normalase. Ninety-six xGen DNA libraries were generated with 10 ng NA12878 gDNA and amplified with xGen Normalase Combinatorial Dual Indexing primers. Libraries were pooled, Pre-Normalase, using equal volumes and the pool quantified by QubitTM (Thermo Fisher) for loading on the IlluminaTM MiSeqTM V2 50 cycle Nano flow cell to obtain percent Reads Identified from each index. The Pre-Normalase pool CV was 15.5%, demonstrating robust and consistent amplification using the Normalase Indexing primers. The same libraries were subjected to Normalase and normalized to 4 nM, Post-Normalase, and loaded on the IlluminaTM MiSeqTM V2 50 cycle Nano flow cell. The Normalase pool CV was reduced to 7.7% showing robust normalization of multiplexed library pools using xGen Normalase. Lines are median and 95% confidence interval.
Better library normalization compared to conventional methods
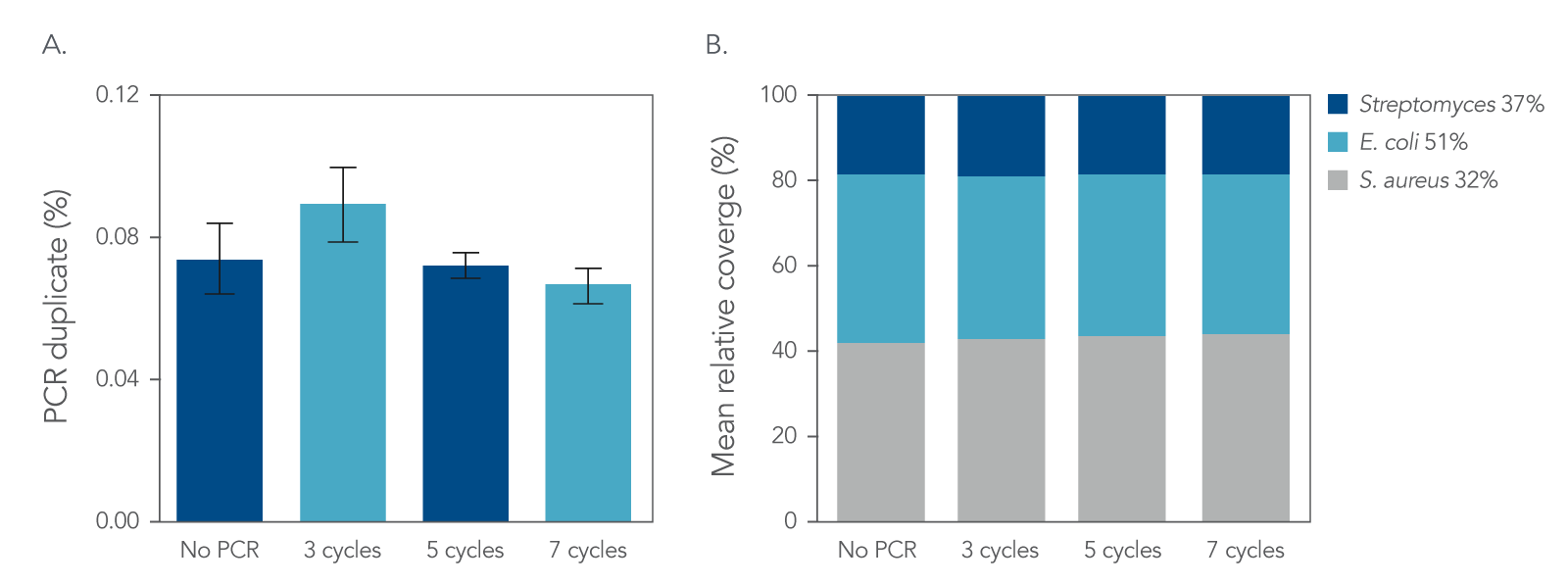
Figure 4. Normalization. IDT xGen DNA libraries were made from 100 ng of DNA consisting of a mix of three reference bacterial strains (E. coli, S. aureus, Streptomyces) mixed at unequal proportions. DNA fragmented to 350 bp was ligated with full-length indexed Y-adapters, and was either not amplified or amplified using 3, 5, and 7 cycles of PCR using IDT HiFi Polymerase and Normalase terminal primers. All libraries were quantified and pooled based on their qPCR quantification. Libraries were sequenced on a MiSeqTM instrument (Illumina) using PE150 sequencing. Across bacterial genomes with varying GC% content, there was no observed difference in A) the number of read duplicates, or B) genome coverage.
Libraries normalized using Normalase maintain high quality sequencing coverage
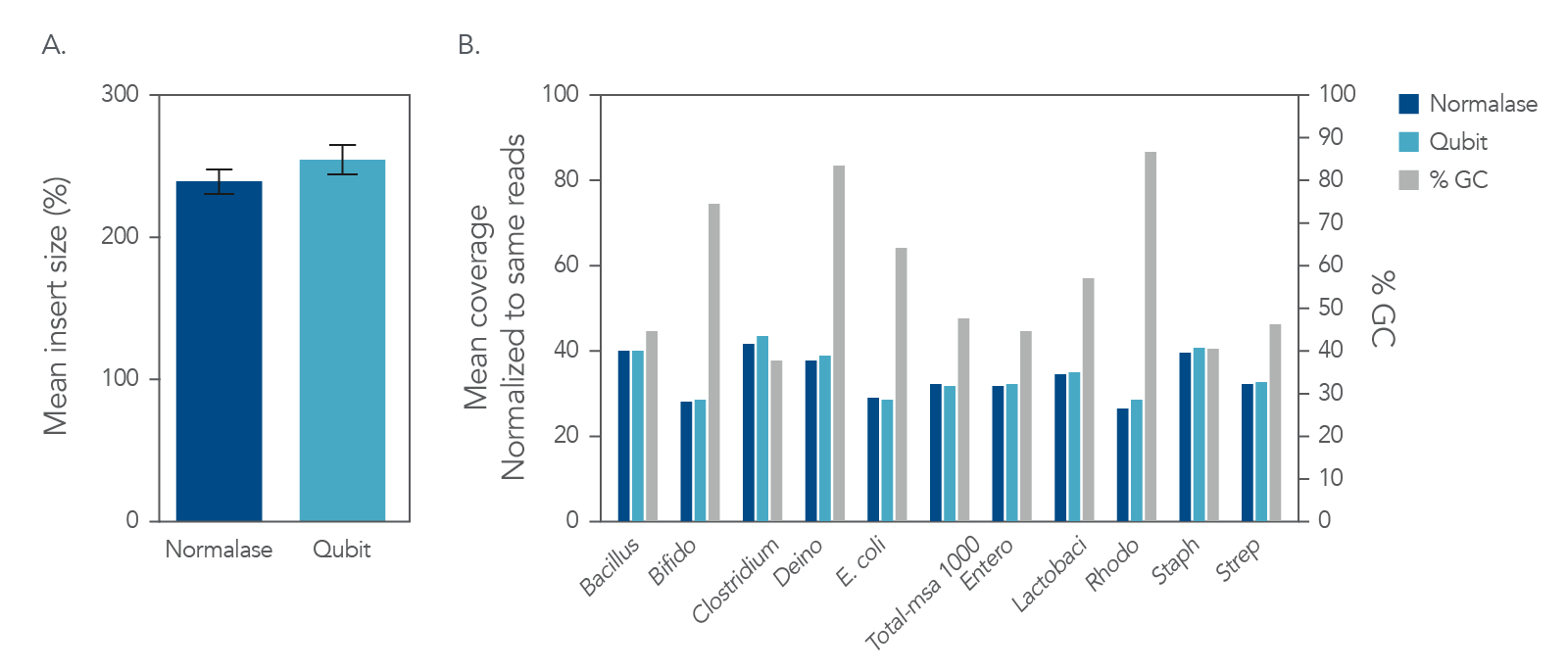
Figure 5. Insert size and coverage. The xGen DNA libraries were made from 5 ng of MSA-1000-an equal mass mix of 10 different bacterial strain genomes with varying GC%. Two libraries were either amplified and indexed with xGen CD Indexing Normalase primers (plum) or IDT CD Indexing primers (blue). Normalase conditioned libraries were normalized to 4 nM and pooled using Normalase, while standard libraries were QubitTM (Thermo Fisher) quantified and pooled at 4 nM. Libraries were co-sequenced on a MiniSeqTM (Illumina) using High Output reagents and PE150 sequencing. Across bacterial genomes with varying GC% libraries, Normalase-treated libraries maintained A) insert size and B) high quality genomic coverage.
Normalase preserves RNA-Seq data quality
To study RNA-Seq data quality (Table 2), four xGen RNA libraries were generated from 50 ng human brain mRNA, amplified, and indexed with either xGen Combinatorial Dual (CD) Indexing primers (n=2), or xGen Combinatorial Dual Indexing Normalase primers (CDI-N), using nine cycles of PCR and IDT HiFi Polymerase. CD libraries were pooled and normalized manually using library quants from the qPCR, while CDI-N libraries were subjected to Normalase up to 4 nM. The two pools were combined and sequenced on a MiniSeqTM (Illumina) High Output (2x150) run. Sequencing data were normalized to 4,011,853 paired-end reads, mapped using STAR, and analyzed for RNA-Seq metrics using Picard (Table 3).
Table 2. RNA-Seq data quality analysis.
| Sample Pooling | Exonic Rate (%) | Intronic Rate (%) | Unique Rate of Mapped (%) | Duplication Rate (%) | Estimated Library Size | Transcripts Detected | Genes Detected | Fragment Length Mean (bp) | Strandedness (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qPCR | 54.57 | 36.22 | 95.50 | 4.50 | 41,387,519 | 94,895 | 17,061 | 162 | 97.33 |
| qPCR | 54.56 | 36.23 | 95.48 | 4.52 | 41,228,061 | 94,960 | 17,129 | 161 | 97.31 |
| Normalase | 54.50 | 36.32 | 95.58 | 4.42 | 42,333,797 | 94,608 | 17,091 | 159 | 97.28 |
| Normalase | 54.49 | 36.34 | 95.57 | 4.43 | 42,208,180 | 94,711 | 17,107 | 158 | 97.28 |
Table 3. Coverage metrics of the top 1000 expressed transcripts showing no differences between qPCR manual pooling and Normalase.
| Sample | Mean Per Base Cov. | Mean CV | No. Covered 5' | 5' 200 Base Norm | No. Covered 3' | 3' 200 Base Norm | Num. Gaps | Cumul. Gap Length | Gap % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qPCR | 273.90 | 0.90 | 860 | 0.27 | 948 | 0.45 | 669 | 63701 | 4.65 |
| qPCR | 278.39 | 0.90 | 864 | 0.26 | 954 | 0.45 | 639 | 62079 | 4.68 |
| Normalase | 277.33 | 0.91 | 859 | 0.26 | 944 | 0.45 | 661 | 64419 | 4.82 |
| Normalase | 275.19 | 0.91 | 866 | 0.27 | 944 | 0.45 | 650 | 61794 | 4.58 |
Specifications
| Feature | xGen Normalase Module |
|---|---|
| Post-library amplification molarity required prior to Normalase | 3x target molarity in 20 µL |
| Normalized concentration Post-Normalase |
4 nM (or 2 nM when using ≥ 6 nM normalization workflow option) |
| Library compatibility |
|
| Library balance within a pool | Coefficient of variation ≤ 10% |
| IDT indexing compatibility | xGen Adapters xGen Normalase Combinatorial Dual Indexing Primers xGen Normalase Unique Dual Indexing Primers |
| System compatibility | Consistent results across Illumina sequencing instruments |
- Save time and increase throughput: Uniform sampling with fewer handling steps to generate balanced library representation for multiplexed sequencing of research samples.
- Reduce sequencing costs: Improve library balancing, allow higher multiplexing per run and obtain predictable read numbers.
- Flexible design: Compatible with diverse DNA and RNA library preparation methods to produce more evenly balanced sequence data.
- Simple, 45-min protocol
- Workflow design for easy high-throughput research sample processing (automation systems)
xGen™ Normalase™ Module
Core kit for performing Normalase, includes Normalase I and Normalase II reagents and Normalase terminal primers, Normalase indexing primers sold separately.
xGen™ Normalase™ UDI Primers
Premixed, unique dual index primers designed for Normalase™ workflow. Individual plates of 96 indexes or sets of 384 indexes are available. Or choose all four sets for a total of 1536 index pairs. All plates are single-use to minimize the risk of contamination by multiple handling events.
xGen™ Normalase™ CDI Primers
Combinatorial dual index primers designed for Normalase workflow. Consists of 20 individual tubes of indexes that support up to 96 combinations of i7-i5 indexes.
 Forgalmazott termékeink gyártói - keressen gyártó szerint a logóra kattintva
Forgalmazott termékeink gyártói - keressen gyártó szerint a logóra kattintva